EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USService Chaining
Service Chaining: This method is used to allow data traffic to reroute through one or more services such as firewall, Load balancer, and IDP devices.
Services in Network:
Firewall, Load balancer, IDP can be installed centrally or remotely in both form factor that is virtual and physical and network traffic must be rerouted from any location to these services for following reasons:
- Traffic from less secure regions must pass to these services to ensure they are not altered.
- If there are multiple VPN in network, and each represent BU or different organization traffic, in send traffic between VPNs, they must traverse through Firewall
- In order to load balance the traffic it must traverse through load balancer
Provisioning Services in Viptela Overlay network:
From vSmart controller, a service chaining can be orchestrated by Network Admin. There is no configuration required of any vEdge router.
Let’s see what the general flow of Service Chaining is:
- vEdge routers advertise services available in their network (branch or campus ) to vSmart controller
- vEdge router also advertise TLOC and OMP routes to vSmart controller
- For any traffic that require that service , policy on vSmart controller changes the next hop for OMP routes to service landing points and traffic is first seen by service and then routed to final destination
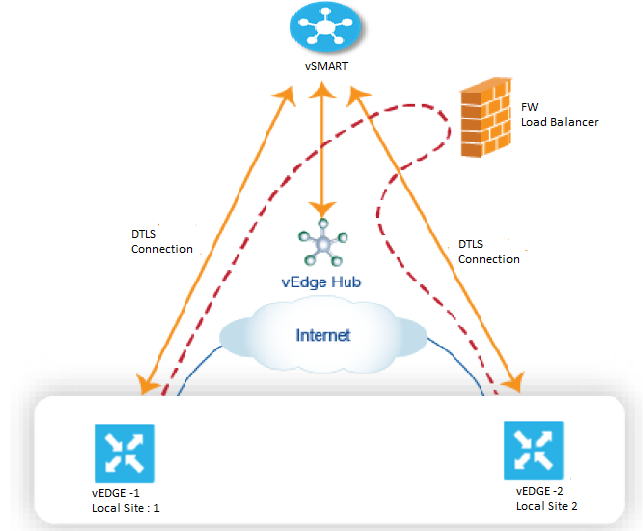
Let’s see in below dig, that a centralized HUB vEdge router is connected to two branch router and a control policy is implemented which says that traffic from branch 1 to branch must travel to vEdge Hub router service . Now Traffic from Branch 1 will go to Hub Firewall service and from there it will return to Hub and then from hub it will reach to Branch 2 destination at site 2.
Service Route SAFI:
The Branch and HUB advertises the Services available in their site to vSmart using service route via OMP.
The vSmart controller maintains the service routes in their RIB and they don’t propagates these routes to any vEdge.
Each service Routes SAFI has following attributes:
- VPN ID (vpn-id)—identifies the VPN that the service belongs to.
- Service ID (svc-id)—identifies the service being advertised by the service node. The Viptela software has the following predefined services:
- FW, for firewall (maps to svc-id 1)
- IDS, for Intrusion Detection Systems (maps to svc-id 2)
- IDP, for Identity Providers (maps to svc-id 3)
- netsvc1, netsvc2, netsvc3, and netsvc4, which are reserved for custom services (they map to svc-id 4, 5, 6, and 7, respectively)
- Label—For traffic that must traverse a service, the vSmart replaces the label in the OMP route with the service label in order to direct the traffic to that service.
- Originator ID (originator-id)—The IP address of the service node that is advertising the service.
- TLOC—The transport location address of the vEdge that is “hosting” the service.
- Path ID (path-id)—an identifier of the OMP path.
Service Chaining Policy:
Service Chaning policy can be provisioned either by control policy or Data policy, if Control policy is used then match criteria are based on destination prefix, or any of its attributes and if data policy is used match criteria would be source IP, Source Port, DSCP, destination port, of packet or traffic flow.
These policy can be configured by CLI or by vManage.




LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.