EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USTraffic forwarding between remote Leaf pair before ACI 4.1(2)
Before ACI4.1(2) , the options like Remote Leaf Direct traffic forwarding was not enabled , due to which all the traffic between Remote leaf pair gets forwarded through Spine from ACI main Pod.
Below figure explain End point learning between Remote Leaf pairs before ACI release 4.1(2) without Remote Leaf Direct feature.
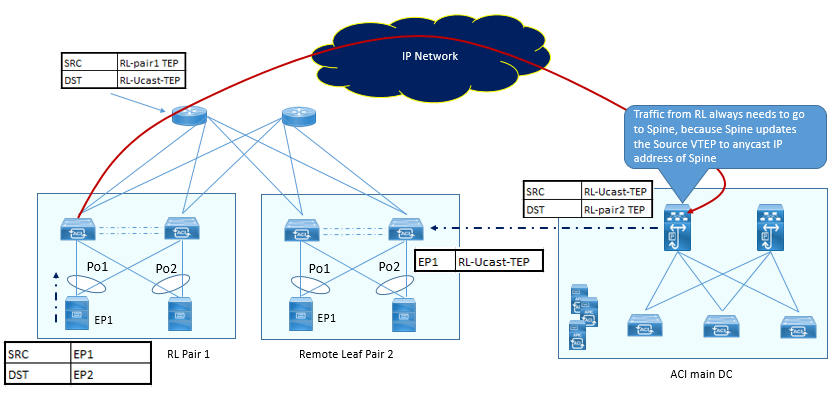
In the above figure, EP1 connected to Remote Leaf Pair 1, and EP2 connected to remote Leaf Pair 2.
- When EP1 send the traffic for EP2, the remote Leaf pair 1 upon packet receipt, checks the EP2 information and if it does not have the information in its hardware table, the packet will be sent to Spine, by encapsulating the packet to VXLAN having Source IP RL-pair1-TEP and destination of Spine RL-Ucast-TEP.
- When Packet is received to Spine of Main DC, Spine will check the EP2 MAC reachability Information and if EP2 the information is available to Spine, It will forward the Packet to EP2 with Source IP RL-Ucast-TEP and Destination as RL-Pair2-TEP.
- Once RL-Pair2-TEP switches receives this packet, It will update EP1 reachability information (RL-pair1-TEP) in its hardware table. Now Traffic from EP2 to EP1 will be sent as same manner.
Traffic forwarding between remote Leaf pair from ACI 4.1(2)
Starting from ACI release 4.1(2), traffic between different Remote Leaf can be established directly via IPN rather hair-pinning to main DC Pod.
In Below figure, Remote Location 1 is logically attached Pod 1 and remote Location 2 is directly attached to Pod 2. Traffic between Remote Location 1 and Remote Location 2 is done directly and without hair-pining to Spine.
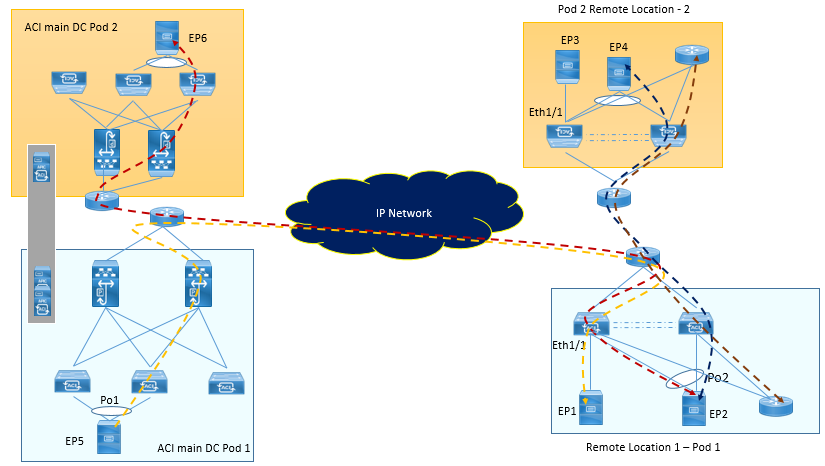
Inorder to achieve this remote Leaf to remote Leaf direct forwarding, following changes were done in Remote Leaf Architecture.
- Remote Leaf will establish VXLAN tunnel to another Remote Leaf associated to same Pod or different Pod.
- Remote Leaf will also form VXLAN tunnel to Spine of Main DC or Spine of all other Pod with in ACI fabric.
- Remote leaf learns the endpoints of all the other Remote leaves and local leaves with the next-hop of the tunnel toward other RLs or toward the spines of other Pods within a single ACI Fabric.
- Remote leaf forwards traffic over these tunnels. Since traffic is being directly forwarded over these tunnels, traffic forwarding from RL to other RLs and local leaves within the ACI Fabric is direct instead of hair-pinning to spines.
Remote Leaf Direct Traffic Forwarding Control Plane
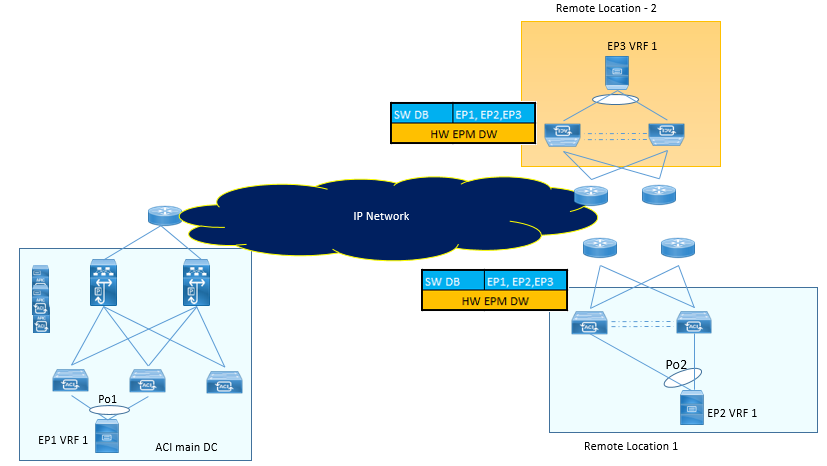
- When EP are connected, Spines learn these EP information from COOP and keeps in its COOP database. Remote Leaf builds the local software Database (SW DB) from this spine COOP database. This SW DB will have all information of Endpoints for all VRF deployed in it.
- Remote Leaf also have hardware Endpoint manager (HW EPM) database that keeps the information about all remote endpoints , which has an active communication between remote endpoint and local endpoint.
- Remote Leaf updates HW EPM database from SW DB based on dataplane communication.
- When Remote Leaf wants to send packet to remote endpoint, it checks remote endpoint (destination) information in HW EPM. If it finds, it will forwards the packet.
- And if HW EPM does not have any entry for destination endpoint, it will check its local SW DB and if the destination entry is present, remote leaf will first updates it HW EPM Database and then forwards the packet.
- But if SW DB has no entry for destination endpoint, RL will either flood or send the packet to spine proxy based on BD setting to discover the silent host.
- Once the Destination Endpoint is discovered, COOP will be updated on Spine and EP information in SW DB will be updated on all remote leafs with in ACI Sites.
Below figure explains the control plane for remote Leaf to remote Leaf direct traffic forwarding
Remote leaf to Remote leaf direct traffic forwarding within or across Pods in a fabric
Below figure explains how Remote leaf to Remote leaf direct traffic forwarding within or across Pods in a fabric is done
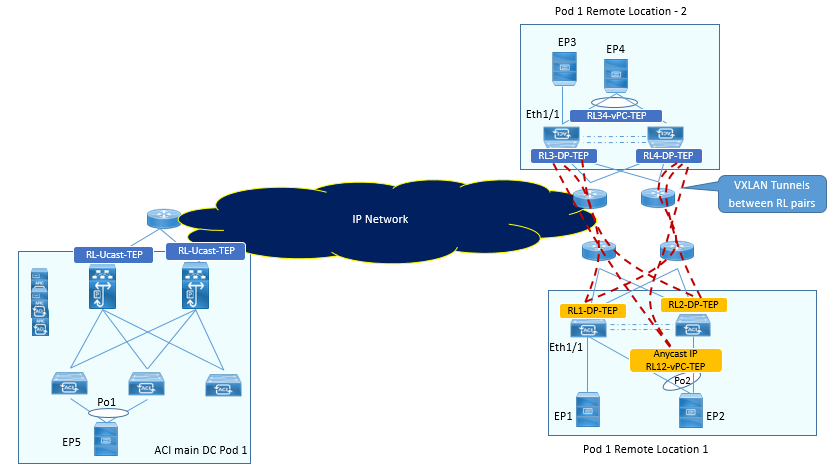
RL1, RL2, RL3, and RL4 are part of the same ACI Pod. Each RL builds a tunnel to all of the other RLs with the destination “Anycast TEP for vPC” to send traffic to EPs that are connected using vPC.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.