EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USACI Evolution
As we know that ACI have been evolved from ACI 1.0 to ACI 5.X, and will still be evolving to further releases. Cisco ACI Remote leaf is the latest development which provide policy domain extension to satellite DC.
Below figure demonstrate the ACI Evolution
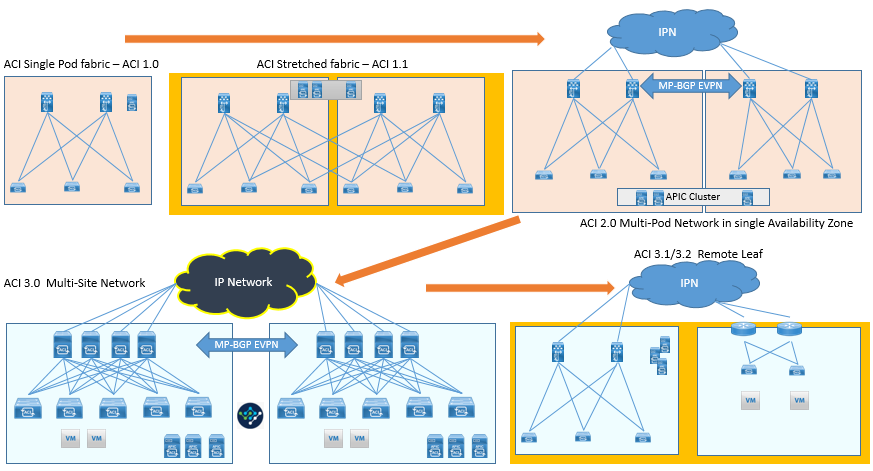
In ACI release 1.0, it has Spine and Leaf (Single Pod) Architecture, where Leaf nodes are fully meshed with spine nodes. Entire Pod is managed with Single APIC Cluster and is mostly deployed in Single DC.
With ACI release 1.1, it gave flexibility to stretch a Pod across separate Physical DC location mostly in same metropolitan area. In this Architecture, Some Leaf nodes also called as transit nodes are connected to both Local and remote spine node. Still this is a stretched fabric, but it represent a single Pod deployment, where a single APIC cluster is used to manage the ACI fabric control plane and Policy Management and creates a single failure domain.
But using the Stretched fabric domain, it also extend the single network fault across entire stretched fabric. To address this concern, ACI release 2.0 introduced the ACI Multipod Architecture.
In this Architecture, ACI fabric is deployed in different multiple Pod, where each Pod runs its own instance of Control plane and is interconnected through external IP routed network. Even though they are part of different POD and represent a single fabric, but still it provides full resiliency. The Maximum Latency (RTT) should be 50 msec between different Pods.
Even though ACI was developed to isolate network fault domain of Stretched fabric, but still complete isolation between Pods was not there. So Inorder to provide complete isolation across different ACI network, ACI Multi-Site was developed.
ACI Multi-Site was developed in ACI release 3.0, which helps to provide connectivity between two different ACI fabrics and is managed by MSO.
Even though ACI Multi-Site is used to connect two different ACI fabric spanned across different geographical area, but if we want to extend the ACI policy in remote location (small or Satellite Area) with either multi-Pod or Multi-Site, it was not desirable to invest.
Inorder to provide solution of this issue, with ACI release 3.1 onwards, a new solution of Remote leaf was developed. With Remote Leaf Solution, ACI controller called APIC present in main datacenter is used to manage and extend policy across remote leaf deployed in remote site. Remote Leaf uses generic IP network to connect to main DC APIC domain. In Remote leaf solution, only leaf switch are deployed while spines are in main DC.
Remote Leaf Use-Cases
In order to understand remote-leaf use cases, Lets understand business values of Remote leaf Solution.
Following are key business values of remote leaf solution.
- Extension of ACI policy model from Main DC to remote sites or DC over same IP backbone.
- Extension of ACI fabric to a small DC without much expense in full-fledged ACI fabric
- Centralized Policy management and control plane for remote locations
- Small form factor solution at location with space constraints.
Below are some use case that can be achieved via Remote leaf
- Satellite/Co-Lo Datacenter: When Customer has main DC are many small/Satellite DC are distributed across multiple location. Using remote Leaf, Satellite DC can be managed with same Network & Security Policy, Monitoring, telemetry, troubleshooting policy as Main DC.
- Extension & Migration of DCs: During migration, if requirement to migrate the workload between DC over DCI via vMotion. Remote leaf allow to expend Layer2 domain from Main DC to remote DC.
- Telco 5G Distributed DC: In order to provide Services near user, Edge are being deployed and to provide the same network & Security Policy & Operation management, remote leaf are used.
- Disaster Recovery: Even though, Remote leaf loose connectivity to all spines, all services running in remote Leaf will continue to work.
Remote Leaf Architecture Overview
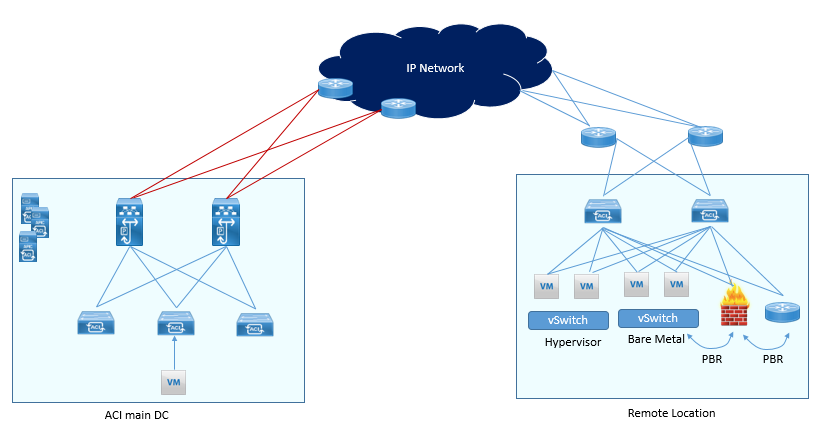
In Remote Leaf Architecture, all APIC controllers, Spines are at main DC and Leaf Switches are at remote DC location. The Spines and Remote leaf are connected over IP network. All the Remote Leaf discovery, configuration, pushing policies are done by APIC cluster from main DC.
Remote Leaf connects to spines of main Pod over VXLAN tunnels.
Below figure demonstrate the ACI Remote Leaf Architecture
Below are some feature provided by remote leaf Solution:
- Remote leaf connects to Virtual Servers, Physical Servers, and Containers.
- Firewalls, Load balancer, routers, or any other services can be connected to Remote leaf similar to local Leaf Switch like in Main DC.
- ACI Service Graph are used to perform service chaining for main Main DC and ACI remote leaf solution. (Currently Un-managed Mode service graph is supported.
- L2 Extension on remote leaf can be done by using static EPGs.
- L3out to provide external connectivity is also possible on remote Leaf.
Before ACI release 4.1(2) traffic from remote leaf were hair pinned to main DC and then to other remote location.
But from ACI release 4.1(2), each remote Site can directly communicate to other remote site with being hair-pinned to Main DC.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.