EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USL2 External Network with ACI
This topic will help you to understand how and what methods are used to extend the layer 2 network outside the ACI fabric.
There are various methods extend the layer 2 domain beyond ACI fabric.
- Extending the EPG out of the ACI Fabric: An EPG can be extended out of ACI fabric by statically assigning port to an EPG. As soon as leaf receives the traffic and determines the end point information, it assigns the traffic to Proper EPG by matching the VLAN ID on port.
- Extending the Bridge Domain out of the ACI Fabric: It is also possible to extend the bridge domain by creating the layer 2 outside connection (External Bridge network). By doing so, it extend the bridge domain to the outside network.
Now we will be discussing the both above scenarios in detail.
Extending the EPG out of the ACI Fabric:
An EPG can be extended out of ACI fabric by statically assigning port with VLAN ID to an EPG. Once it is done traffic received on the leaf port which is configured in particular VLAN ID, will be mapped to the EPG and the policy for this EPG will be enforced to leaf switch. END points can be directly connected to leaf ports or it can be behind a layer 2 network and is connected to ACI fabric.
To configure the port to an EPG, we have to follow the following steps:
- Go to Tenant -- Application Profiles – EPG – Static Port.
- Click the ACTION menu to assign the port to an EPG.
Below example shows interface eth1/15 from leaf node 101 is assigned to VLAN 10 which is WEB EPG.
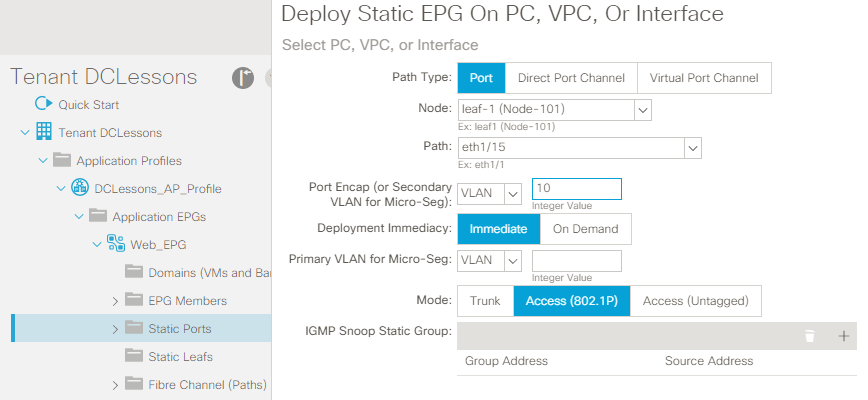
Here there are Some option available:
- Deployment Immediacy: It means when actual configuration will be applied on leaf switch, its related configuration and policy will be programmed right away. And the Option ON-Demand will enforce the EPG and its related Policy on leaf switch hardware only when data frame is received for this EPG.
-
Intermediate: It means that as soon as EPG configuration and its policies are configured in APIC , these will be programmed to Leaf Switch right away.
-
ON-Demand : with this option , APIC will deploy configuration and policies related to it on leaf switch, only when traffic matching this policy & its related EPF is received.
Mode: Mode has three options, Trunk means the port will be configured as Trunk port, if it is trunk port then it will except the received frame tagged with VLAN ID. Access (802.1P) means Leaf will except the frame untagged.
- Trunk: The Trunk option means that the leaf node expects incoming traffic to be tagged with the specified VLAN ID previously established. This is the default deployment mode. Choose this mode if the traffic from the host is tagged with a VLAN ID. Multiple EPGs can be statically bound to the same interface as long as the encapsulation VLAN/VXLAN ID is unique. This is similar to the switchport trunk allowed vlan vlan_ID command.
- Untagged: The Untagged option means that the leaf expects untagged traffic without a VLAN ID. Much as with the switchport access vlan vlan_ID command, with this option you can assign the interface to only one EPG. This option can be used to connect a leaf port to a bare-metal server whose network interface cards (NICs) typically generate untagged traffic. A port can have only one EPG statically bound to a port as untagged.
- 802.1P: The 802.1P option refers to traffic tagged with 802.1P headers. 802.1P mode is useful when it’s necessary to handle the traffic on one EPG as untagged to the interface (much as with the switchport trunk native vlan vlan_ID command), but, unlike the untagged mode, 802.1P allows other tagged EPGs to be statically bound to the same interface
The Following figure is the USE case or various ways of extending EPG to Outside Network:
- Option 1: Connecting Physical Server to ACI fabric
- Option 2: Connecting Hypervisor Platforms like Xen , KVM integrated with APIC to ACI fabric
- Option 3: Connecting legacy Ethernet network to ACI , which connect the legacy Ethernet network of DC
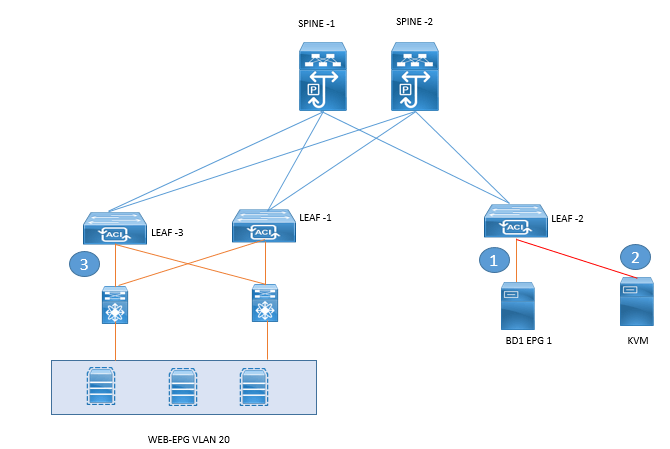
- For Legacy network, each of the VLAN in the legacy network will be mapped to an EPG in the ACI fabric, ACI leafs will provide the Layer 3 forwarding between VLANs by enforcing contracts between EPGs.
- All Endpoints which are learned on the non-fabric uplinks are stored on Local Station tables and Endpoints (remote endpoints) that are learned on fabric uplinks ports are stored on global station table.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.