EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USQOS on Nexus 7000 switch Modules
In the core datacenter layer switches usually COS and DHCP marking are not required because mostly these marking are done at access layer or Virtual access layer switches. In this case core layer has main responsibility to manage packet loss and core layer should trust the CoS and DHCP marking on ingress and perform the ingress and egress queuing.
In Nexus 7000 Switches, there are F and M module both supports QoS out of which we will see the differences in architecture and capabilities between these two M2/F2 Modules.
Nexus 7000 supports following QoS policies:
- Qos: This policy is used for marking and policing.
- Network-qos (required on F-Series modules only): Defines the characteristics of network-wide QoS properties and should be applied consistently on all switches participating in the network.
- Queuing: This policy is used for queuing and scheduling.
Nexus 7000 trust the QoS marked traffic by default according to following rule:
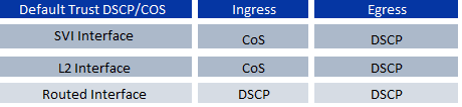
- For (L2) bridged traffic, CoS is used for ingress queue selection and DSCP values which is received is transmitted unmodified and are ignored from a QoS perspective. The received CoS markings are used for egress queue selection and are also transmitted unmodified on egress bridged ports.
- For (L3) routed traffic, CoS is used for ingress queue selection; DSCP markings are not modified, but are used to generate new CoS markings derived from the 3 Most Significant Bits (MSB) of the DSCP; these newly generated CoS markings are then used for egress queue selection even if the egress interface is not an 802.1Q trunk and so not carrying CoS within the frame.
Let’s now understand the Nexus 7000 M2 Qos Architecture and Concepts:
Nexus 7000 M2 Module: QoS Design & Architecture
Below figure describes the Nexus 7000 M2 Series Module architecture and also labels the QoS policies applied.
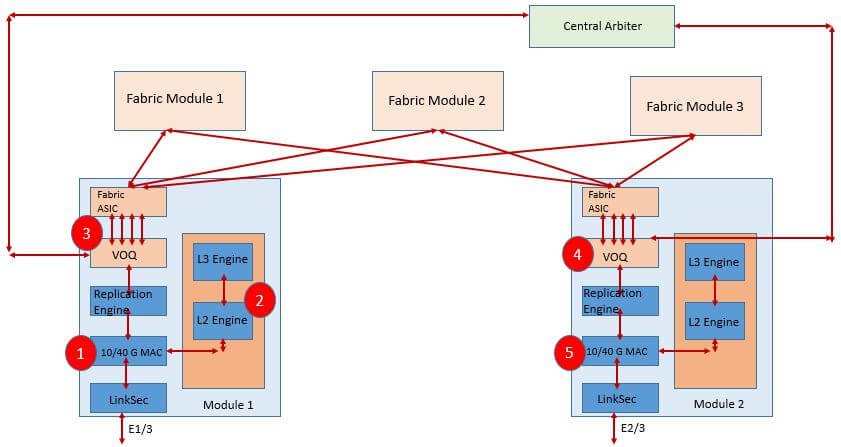
In Nexus 7000 M2 Modules following are QoS policies applied in marked places in above diagram:
- Ingress (type queuing) policies are applied at the ingress physical port.
- Classification, marking and policing (type qos) policies are implemented within the forwarding engine.
- Fabric QoS policies are applied in the VOQs beforethe packet traverses the three-stage switching fabric.
- Egress (type queuing) policies are applied in the VOQs afterthe packet traverses the three-stage switching fabric.
- Egress (type queuing) policies are applied again in the egress physical port.
Here ingress and egress QoS policies can be configured manually or used default but fabric Qos for VOQ Queuing is not configurable and is made standard across nexus 7000 Series.
You have learned how VOQ works in Module 1 Hardware chapter, so here we are only giving snapshot of it. As soon as Qos Marked traffic inters in to Module based on its Ingress queuing policies which will be described later in this chapter, packets are queued in VOQ as per following table:
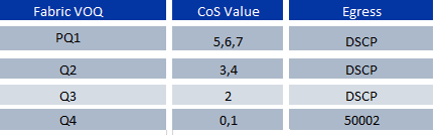
PQ1 is strict priority queue and Q2 to Q4 are scheduled with weighted Round robin (DWRR) and are assigned equal weights. These above mappings are static and are not configurable. Once central arbiter grant the permission the Packet from ingress module VOQ will be sent across to Fabric Module and are queued in to Egress VOQ queue and then is scheduled according to its marking and queue priority weight to be queued to Egress Queue by egress Queuing policy and then finally transmitted to output interface.
Below figure described each stage queuing function:
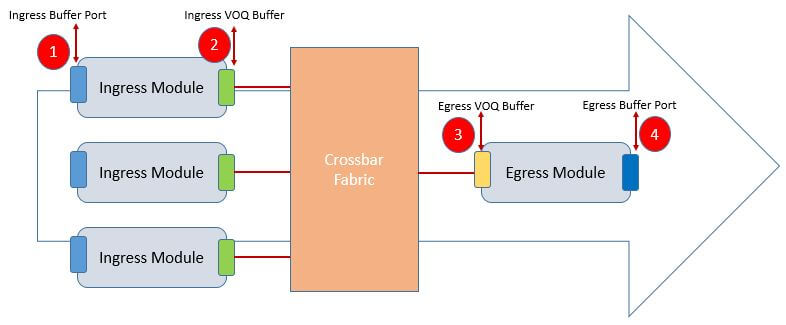
- Ingress port buffer:Manages congestion for ingress forwarding/replication engines
- Ingress VOQ buffer (fabric queue):Manages congestion toward the switching fabric
- Egress VOQ buffer:Receives frames from the fabric and manages congestion for multidestination frames
- Egress port buffer:Manages congestion at the egress interface
Now let’s understand how ingress and egress queuing is done in Nexus 7000 M2 module.
Nexus 7000 by default trust the CoS and DSCP value on ingress and there are two steps to configure QoS on M series module
- Configure Ingress Queuing
- Configure Egress Queuing
Now each Nexus 7000 M2 series module supports following types of ingress and egress QoS structure. Nexus 7000 supports four class (4Q2T ingress and 1P3Q4T egress) model and eight class (8Q2T ingress and 1P3Q4T egress) model
For Eight Class QoS model:
- On Ingress: 8Q2T ingress Queuing structure is used
- On Egress: 1P7Q4T egress Queuing structure is used.
The Nexus 7000 uses pre-defined ingress queuing class-maps given in below figure
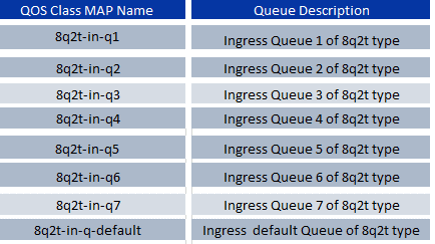
Nexus 7000 also uses pre-defined egress queuing class-map given in below figure:
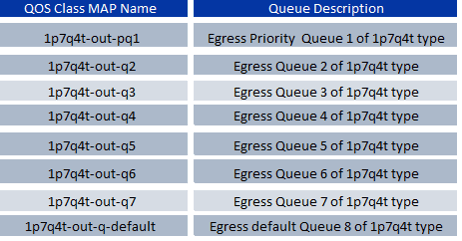
Also queuing feature are enabled by default on nexus 7000 via system defaults policy-maps applied on each interface and port-channel. The default 8Q2T ingress and default 1P7Q4T egress queuing models are given in below figure:





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.