EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USControllers Placements & Challenges
The placement of controllers has specific challenges regarding their reachability, NAT, and so on. By default, an edge device establishes one control channel to each controller, over each transport. You can control this behavior precisely, as required. For each transport, you can decide whether a control connection is established. You can configure this behavior from the GUI either globally or specifically by device (Configuration > Templates > VPN Interface Ethernet). You can also use the max-control-connections 0 interface configuration command to prevent a control connection from being established over a specific transport. Setting the number to 0 achieves this configuration. This configuration is particularly useful in scenarios where the interfaces connected to an MPLS network will never be able to establish the control connections to the vSmart controllers or vBond if the controllers are only reachable through the internet.
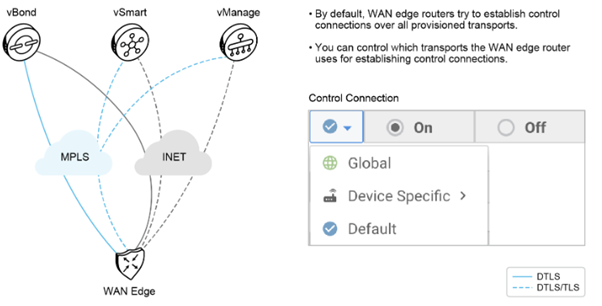
Cloud Controllers Connections
All controllers must be IP-reachable from all devices. First, controllers must be able to reach each other, and then each edge device must be able to reach all controllers. In terms of overall design considerations, various scenarios are implemented in various ways.
Cisco cloud-hosted deployment is the recommended mode of operation. Deployment is easier, because it is orchestrated with Cisco orchestration tools. Customers do not need to worry about design considerations that must be considered in an on-premises deployment. Cisco cloud-hosted deployment is very easy to scale out and provides redundancy of the control plane from the start.
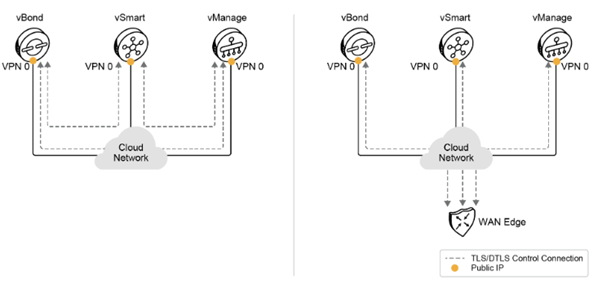
The main requirement is to have internet connectivity from every site. With a single internet connection, however, you have no control plane redundancy.
On-Premises Controller Connections
Over the MPLS cloud, a customer edge (CE) router first terminates the MPLS. From there, normal routing should allow connectivity to the controllers. Routing could be over another network, such as a data center core device or network. Depending on the setup, a firewall might be in the way, between MPLS and the data center.
Especially for an on-premises deployment, you must be careful in vBond placement. If the vBond is placed correctly so that it can detect all NAT functions, NAT traversal is managed automatically.
Both of the following scenarios are supported:
- MPLS cloud and internet cloud are connected.
- MPLS cloud and internet are kept separate.
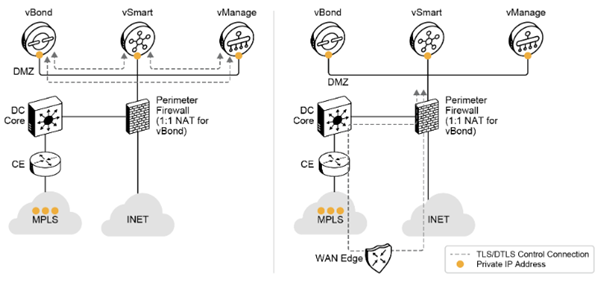
Cloud-Hosted Controllers: MPLS and Internet Connectivity
One design factor is determining whether the MPLS transport and the internet are connected (in other words, if the MPLS cloud has generic internet access).
If the MPLS transport has a connection to the internet, an edge device can establish control connections through both transports.
If not, the controllers are reachable only through internet transport, and each edge device has only a single control connection to the controllers. Therefore, if a local fault makes the internet unreachable in a location, controllers are lost. (However, the data plane traffic can still go through the MPLS cloud, which is described in the topic on high availability.)
In the first deployment, the internet transport is reachable from the MPLS transport through an extranet or a direct-connect connection, so the WAN Edge router can connect to the controllers directly from both transports. For this, the MPLS cloud may be advertising the publicly routable IP addresses of the controllers, or a default route, depending on the network.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.