EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USTroubleshooting in Cisco ACI
Troubleshooting is a structured process used to identify and resolve the root cause of a problem. A problem is defined as the gap between expected behavior (how a function, process, or feature should operate) and observed behavior (how it is actually operating). Once the cause is identified, corrective actions can be applied to resolve the issue or mitigation steps can be implemented as a temporary workaround.
When troubleshooting issues in the Cisco ACI fabric, administrators must monitor traffic flows, perform debugging, and detect specific conditions such as traffic drops, misrouting, blocked paths, uplink failures, and other anomalies.
A thorough understanding of both the logical and physical constructs of the Cisco ACI policy model, along with the external infrastructure (such as endpoint placement on physical servers or hypervisors), is essential for effective troubleshooting.
A common approach begins with the external infrastructure. For example, administrators may start at the hypervisor host and inspect:
- Virtual machines (VMs)
- vSwitch configurations and port groups
- Uplinks connecting to the network infrastructure and the Cisco ACI fabric
This layered methodology ensures that issues are systematically traced from endpoints through the logical constructs to the physical fabric, enabling accurate root-cause analysis and remediation.
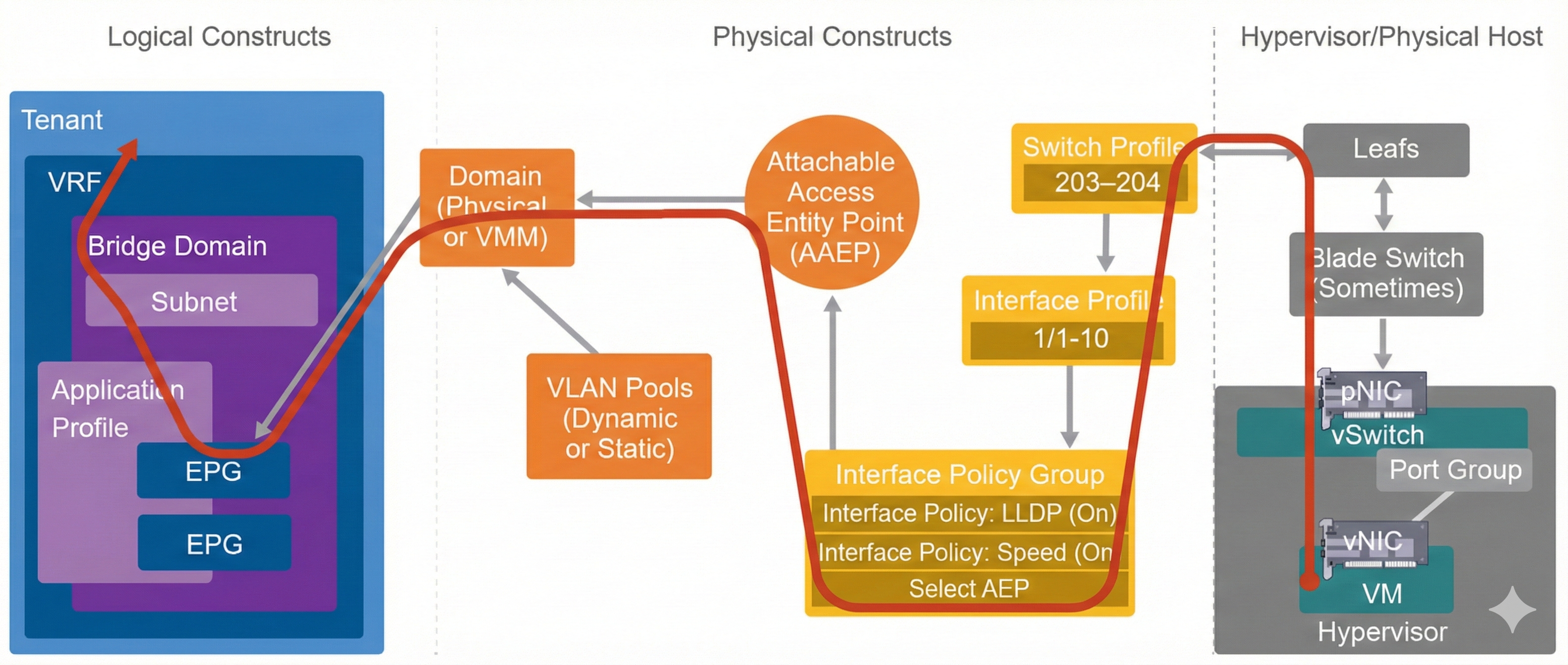
If the physical or hypervisor host connectivity is in order, you can inspect the physical constructs, such as switch and interface profiles, the elements of the interface profiles groups, and the AAEP. The troubleshooting flow should then cover the domain configuration, which can direct the process to the inspection of the logical constructs.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.