EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USPersistence
This BIG-IP F5 Persistence topic will help you to understand and learn all BIG-IP F5 Persistence Configuration used to achive best load balancing methods & Scenerios.
It is used to re-direct the additional request and Connection from a client to same real Server as per the initial connections.
Below are some example of traffic in which Persistence is generally used: Web applications, SIP & Other Voice Technologies, Remote Access.
BIG-IP F5 Persistence are configured on Virtual Server via Persistence Profile. The BIG-IP F5 Persistence profile direct F5 System, to send request to same initial pool member, based on Persistence Table.
Persistence Method
Below are some Persistence Method used in F5
- Source Address Persistence
- Cookie
- Destination Address
- Hash
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol
- SIP
- SSL
- Universal
Source Address Persistence
In this method, F5 will send all the Connection of Same Source IP address or from Particular IP Subnet to same real server.
When a client connects to Virtual Server, it checks to Persistence Table, so see if there is existing BIG-IP F5 persistence record available for same Client IP or Same IP Subnet, if any match is found, F5 will send the traffic or direct the traffic to same pool member specified in Persistence record.
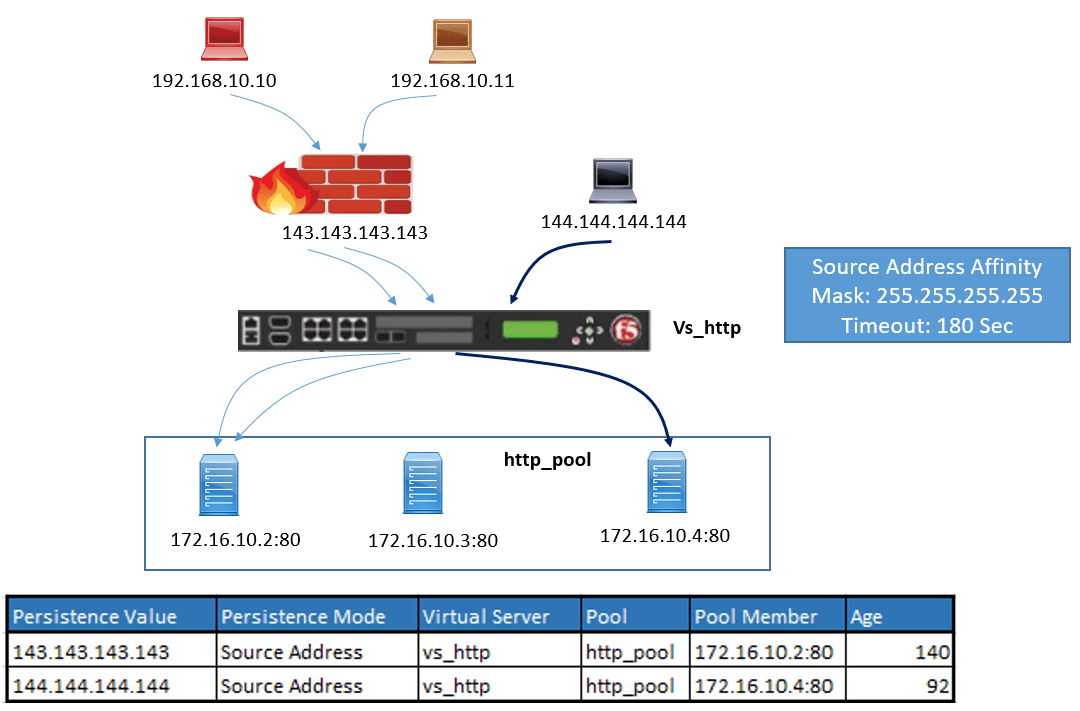
If there is no Persistence record, that matches the Client IP address, F5 will load balance the traffic based on load balancing algorithm. Persistence Record contains following information:
- Persistence Value: IP address or range for which Persistence Applies
- Persistence Mode: Persistence Method being used, in this case Source IP address
- Virtual Server: VS the Persistence record applies to...
- Pool: Name of the Pool , that pool member belongs to
- Pool Member: Node IP address and its Service Port
- Age: How long persistence record has existed.
F5 will direct the traffic to same pool unless:
- There is timeout of Persistence Record
- Pool member or node fails a health Monitor
- Pool Member or node is in forced Offline state.
Persistence Record Idle Timeout
Each Persistence Record is made available to Persistence table for Specific amount of time, if that Record is not being used within that time period, then that record is deleted from F5 Persistence table. This Time out time is said as Persistence Record Idle Timeout.
The default Idle-Time Out is 180 s or 300 s depending on the method used. In good Practice, idle-timeout value should be 300s for TCP and 60s for UDP.
Once Persistence record is created, its age value starts incrementing till configured timeout value, and if that value matches, then that Persistence record is deleted from persistence table.
Persistence Mask Setting
When we use Source Address Persistence Method, F5 creates the persistence record of mask 255.255.255.255. That means IP address 143.143.143.143 and 144.144.144.144 will each have their own persistence record.
Using this, there might be some performance Issue on F5, so if we using mask like 255.255.255.0 then only one persistence record will be there in Persistence table.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.