EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USAdvance Monitor Concepts
Monitors Types:
Below are some advance Monitors types that can be configured in F5 Systems.
- Address
- Applications
- Contents
- Performance
- Path
- Service
Let’s talk about some of the Monitors mentioned above.
Address Check Monitors:
It sends an ICMP request to the specified IP address and check is passed if response is received. If the Address Check Monitors marks the node as offline, its related Pool Member will also be marked offline. Now once the Monitors marks the Node available, its related pool member will be made available.
Gateway ICMP monitor is the example of Address Check Monitor that can be configured in F5. This Monitor is assigned to Pool Member, and it verifies the IP address of host. The benefit of this monitor is that, when the address check fails it only marks the pool member offline and the Node status does not change.
Application Check Monitors
This Monitor sends multiple commands or request to pool members and then review result response.
Example : FTP Monitor , which connect the server , log using specified credentials and navigate to a specified folder and then download a file to /var/tmp/. If the download is successful, resource is considered as successful.
Let’s understand this as below steps:
- F5 established a TCP Session with the FTP Server, by using TCP 3-Way handshake.
- Once TCP session is established, F5 will log in to FTP Server using credentials
- Once F5 successfully Logins to FTP Server, it will navigate to the folder and request the file specified in the Monitor configuration.
- FTP server will send the file, to F5 device
- If the transfer is successful, F5 will mark the FTP Server as
Content Check Monitors
The Content Check Monitor send the send string as per configuration and when it receives the response back from pool member, it examine the content. If the reply matches the configured received string, it marks the pool member available. If the pool member fails to replay back with in timeout period or Reply does not match with configure response string, F5 marks the server Offline.
Example: HTTP Monitor. Monitor sends GET string like /\r\n, means it only sends GET request to default page of the web server. The receive string is blank with means It does not matter what response you get from server. Once this process completes, F5 marks the Pool Member available.
Using this Process is not vary standard practice, and this default setting must be changed , in this case , a new custom HTTP Monitor with suitable string is to be configured as given below :
- Send String: GET /index.html\r\n
- Receive String: 200 OK
Performance Check Monitors
In this Monitors, F5 uses SNMP DCA which retrieves information by fetching performance data from a server using an SNMP agent.
Using this Performance data, F5 builds UP and assigns each node/pool Member a certain weight. Now this weight is then used when load balancing decisions are made.
Path Check Monitors
This Monitors are also called as Transparent Monitors, and if it determine that traffic is flowing successfully, then Path check monitors is considered to be successful.
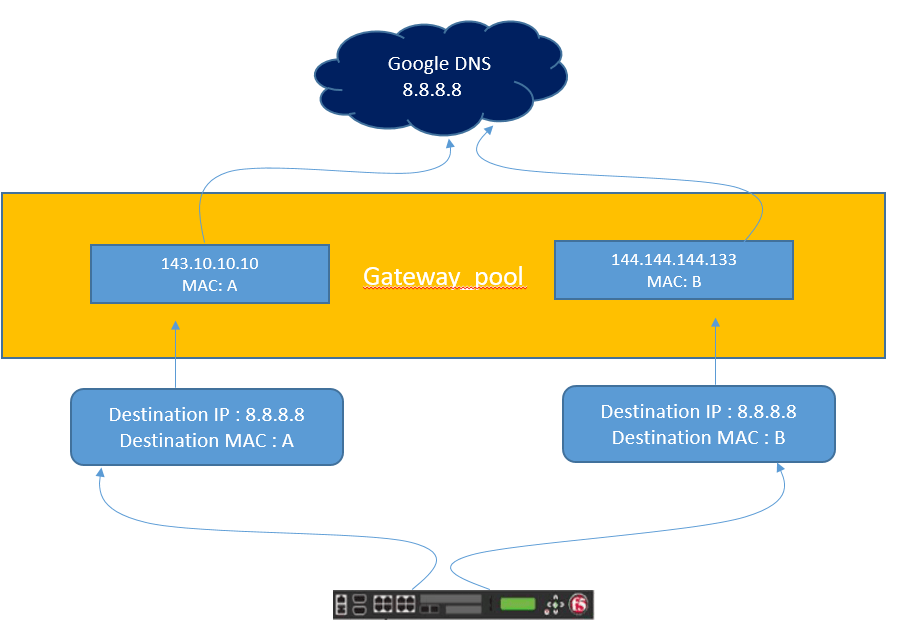
Example: Wen we have multiple upstream gateways (ISPs) configured on F5 system, that resides in gateway_pool. This Upstream gateways route traffic out to internet and acts as pool member in gateway_pool.
Now F5 will load balance the traffic and make sure that upstream gateway (Eq FW) functions correctly for which a monitor must be configured.
Let’s suppose we want to check weather Google DNS 8.8.8.8 is reachable from upstream gateway (FW) or not. TO achieve this we need to configure Gateway ICMP monitor as per below dig
F5-4.1 (use this while doing LAB)
- Under Alias address: configure Google DNS address 8.8.8.8
- Check Yes on Transparent
Now once the above configuration is done , it sends the request to pool member on its layer MAC address but using different destination IP address. Here in this case , it will send ICMP request to Layer 2 MAC address of Firewall but destination address will be 8.8.8.8.
Below Figure show the above concepts
Blow are following monitors that supports transparent Setting
- TCP
- HTTP
- HTTPS
- TCP Echo
- TC Half Open
- ICMP
Object Status
Below are some object status icon, one should know, what does these icon mean.
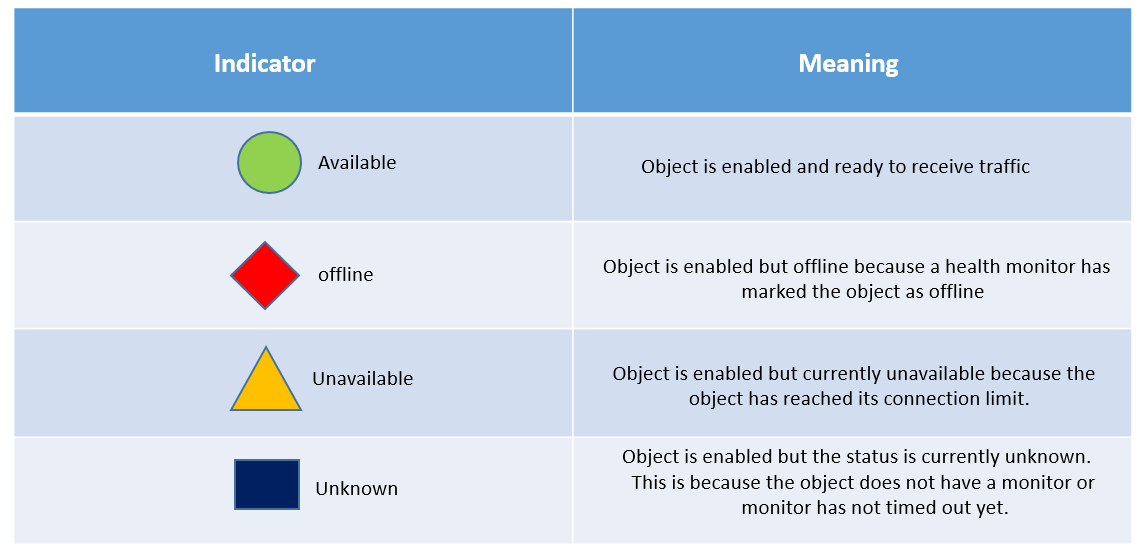
Object State: F5 defines the Object state as per color defined. An administrator can also change the object state for maintenance purpose also. There are currently three objects states.
- Enabled: The Object is available and is ready to receive the traffic.
- Disabled: Object continues to process only existing persistence ad active connection. It will only accept new connection for which it has a current and existing persistence record. It will not accept new connections.
- Forced Offline: The Object continues to process traffic but only existing connections and only if they have not timed out.
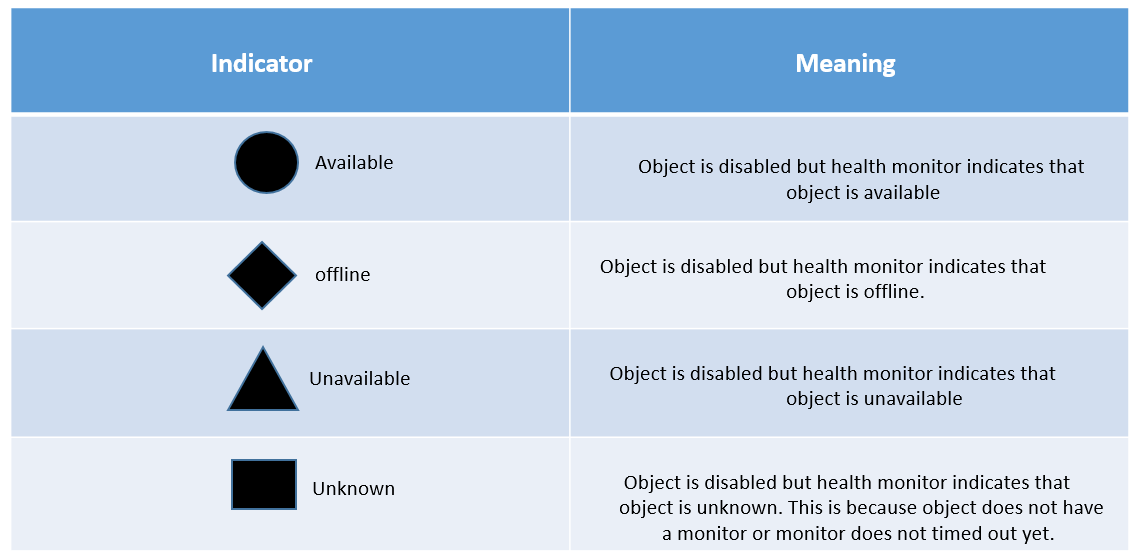
When an object has either been disabled or offline, the color of the status icon is changed to black.
Below are some icon figure, which describes about object when they are in disabled state.
Object Status Hierarchy
Monitors is applied to nodes, pool members, and pools. Monitors has effect on Virtual servers as well, this happens because there is a parent child hierarchy between all these objects.
Below figure explains Monitors Hierarchy?
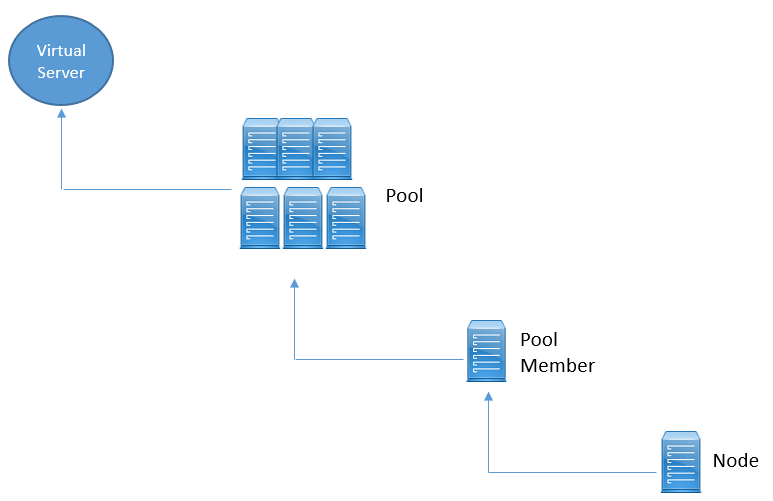
Child object will inherit parents status, means if node is offline, then all of the pool members assigned to that node will be offline.
Now if at least one pool member is available, then pool is available, but of all pool member are offline, pool will be offline. Below figure demonstrate all the concepts.
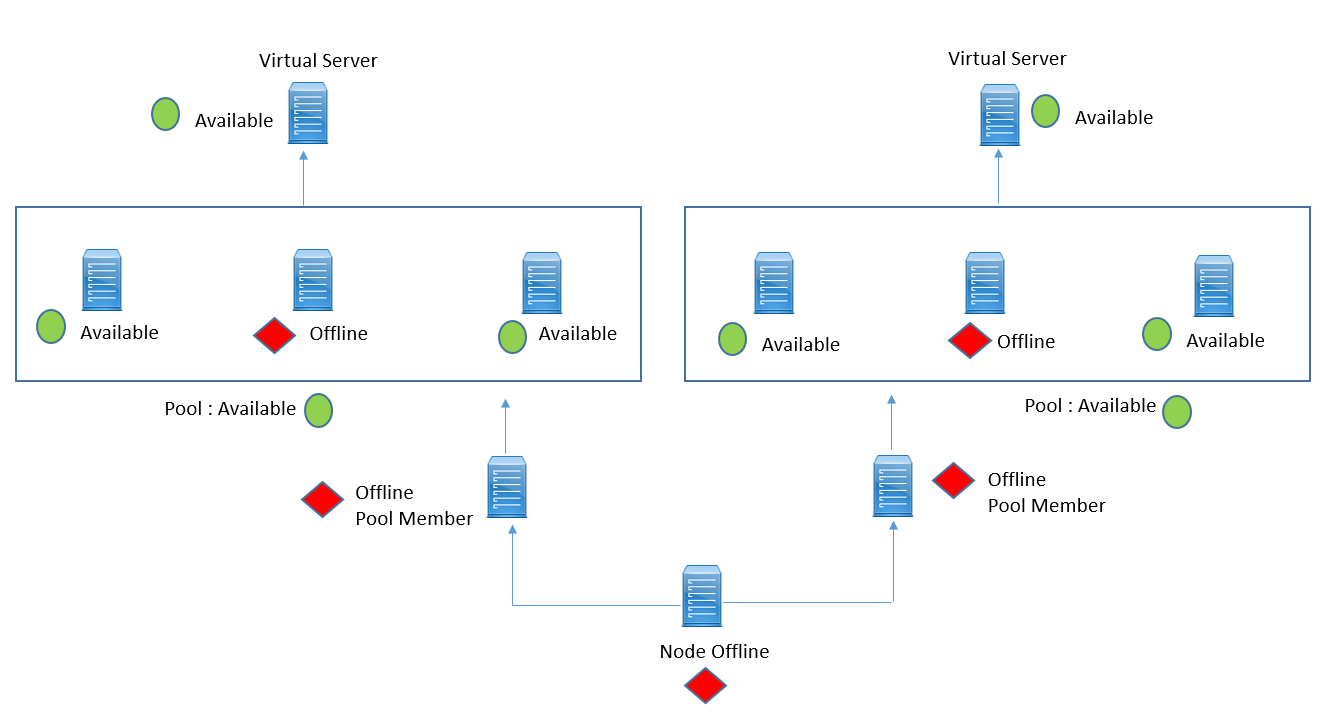
Now let’s discuss some scenarios on the Monitor Hierarchy.
Scenario 1: Let’s suppose, Monitor is applied to both node and pool members, what if Node is available but Pool member seems to be offline.
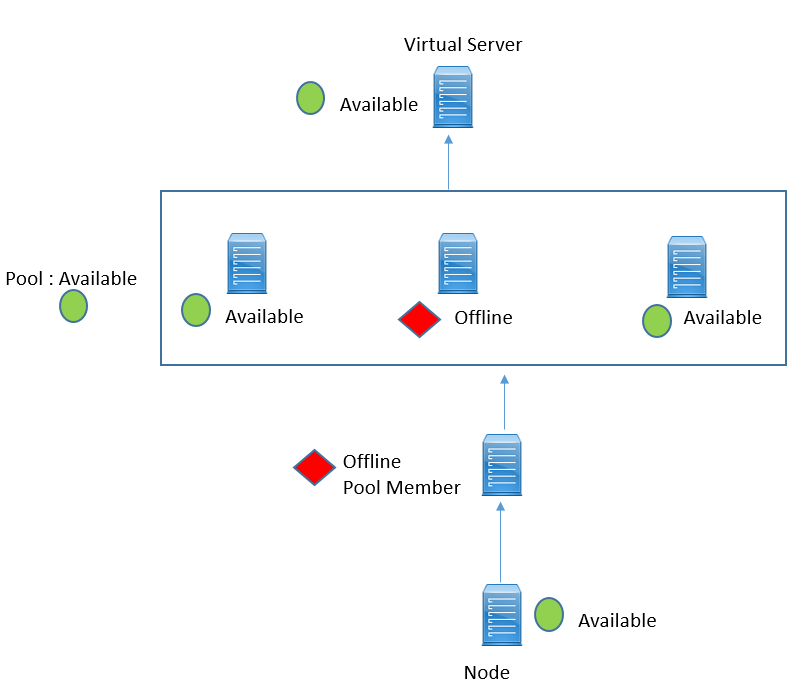
This happens because, Monitor on the node, sending ICMP request and these are successful. However Monitor assigned to Pool Member is verifying the services running on that node is presently offline, which causes monitor to fail, resulting Pool member to be offline.
Scenario 2: In this Scenario, ICMP Monitor assigned to Node is successful, but monitor assigned to Pool Member is unsuccessful, which makes pool member offline. In this scenario, all the other pool member with in the pool are also offline , which makes pool to be marked as offline, and if there is no pool available , its related virtual server also marked as offline.
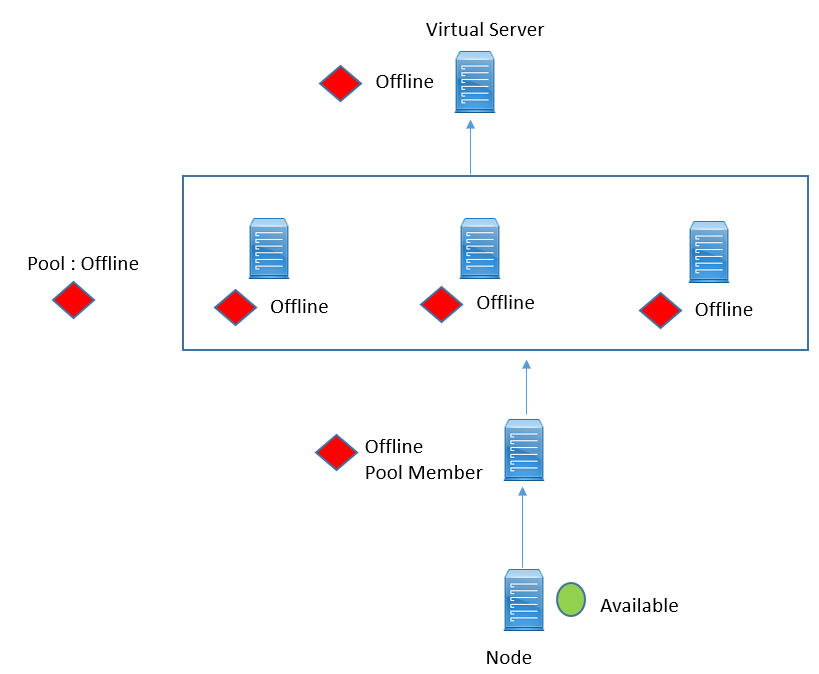




LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.