EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USNAT (Network Address Translation)
When there is requirement to bypass the normal Load balancing selection and to send traffic directly to Server node, we use NAT.
NAT Provides one to one mapping between two IP address, means if an external client sends a request to public IP address, on which NAT is listening. It will then automatically translated to Internal IP address as per NAT Configuration. The same concept applied when internal node tries to communicate to Internet, NAT is applied. Thus it can be concluded that NAT is Bidirectional.
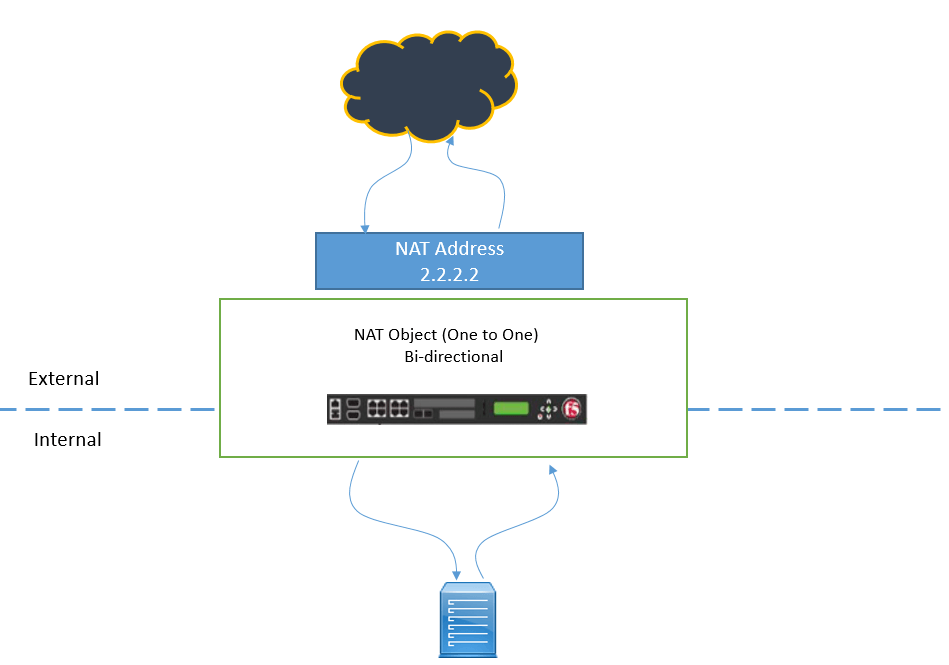
NAT is used to do one to one IP address mapping, but if there is requirement to create many to one mapping, SNAT is used. NAT do not support Port Translation, all ports are open causing potential Security risk because all internal ports are exposed. NAT is also not good for protocols that have embedded IP address in their packets like FTP, NT domain, CORBA IIOP etc.
Traffic Flow using Virtual Server on inbound Connections
Below figure clearly demonstrate when Virtual Server is used as Listener.
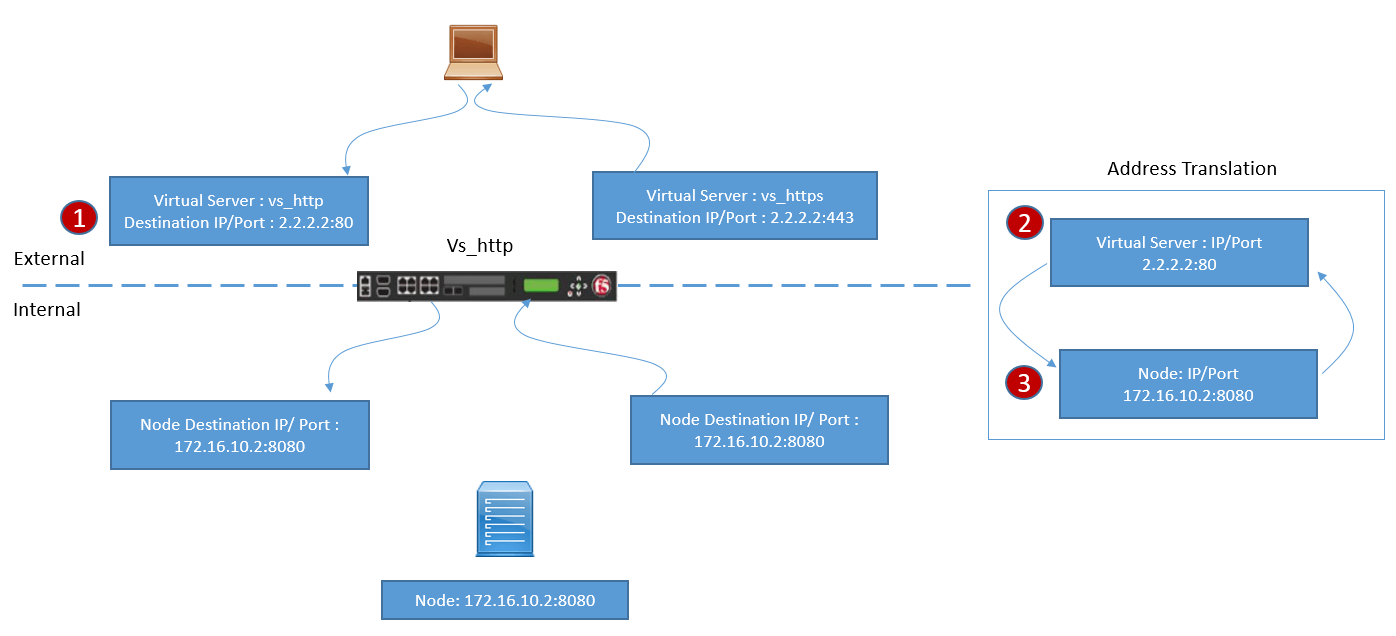
- An External Client sends requests to Virtual Server, which is configured with an IP address and a Specific Port.
- When VS receives traffic, Load balancing decisions are taken, and then pool member is selected. Now F5 will initiate the New Connection from F5 to pool member destination IP address and destination Port. Here Source IP address (Client) will remain the same.
- Pool Member will send reply to F5 and then it will be matched with an existing External session and then F5 will send the packet to client with Source IP of VS External and Destination as Client IP.
Traffic Flow using NAT on Inbound Connection
When there is requirement to establish a connection to an internal server, then in that case we need to translate the destination IP address. IN this case we can use NAT feature.
Below figure clearly demonstrate traffic flow when NAT is used.
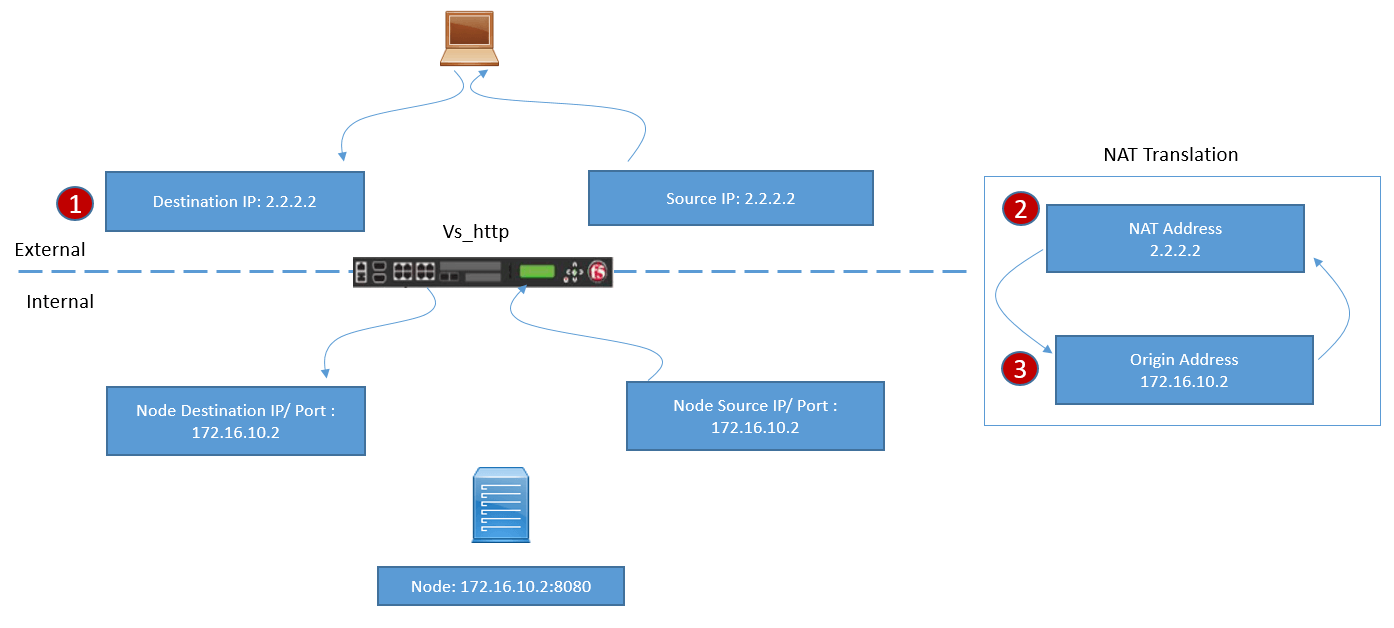
- An External Client sends requests to NAT IP address, which acts as a listener and will match any traffic received on that specific IP address regardless to any port.
- When F5 receives the traffic, it matches against the NAT objects and it translates the destination IP address (NAT address) to private Node IP address. There are no load balancing, Port Translation, applied to traffic.
- When Node Server response back, F5 will reverse the translation formed where Node IP address will be translated to NAT IP address as Source Add and Client origin IP address as Destination IP address.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.