EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USGCP Networking
The Google network comprises of hundreds of thousands of fiber optics cables, running between 85 zones, and 146 Points of Presence (PoP).
With this massive infrastructure, GCP allow customer to connect to GCP at a location very close to your internet Service provider. GCP offers two types of network service tiers:
Premium: It provides high-performance routing. It also offers global load balancing and Content Delivery network (CDN) Service.
This service is used when customer requires global presence and user requires best connectivity experience. This service comes with SLA.
Standard: This service provides lower performance network service with no SLA. The CDN service is not available and Global load balancing is also regional.
When customer focus is more on cost, this type of service can be used. GCP networking is based on Software defined network (SDN) platform called Andromeda , which is the orchestration platform for all network services in GCP.
What is Virtual private Cloud (VPC)
VPC is a remote network configured on GCP to provide all network related service to customer to host their application.
By default, we can configure 5 VPC per project, (Quota can be extended by contacting support). A VPC has a global support and can span in all GCP regions. In VPC subnets are divided into regional subnetworks, that have IP address associated and used to assign address to resources.
When we create a new project, a default network (VPC) is created, subnets are created for each region and have allocated non-overlapping CIDR blocks. By default, Firewall rules are also created, to allow us to ingress ICMP, RDP, and SSH from anywhere. Any traffic within default network is also allowed.
Once we create a VPC, there are two modes, which we can choose:
Auto Mode: Automatically creates one subnet per region with predefined IP range /20 mask from the 10.128.0.0/9 CIDR blocks. Each subnet is expendable to the /16 mask.
Custom mode: In this mode, no subnets will be created automatically and delegates complete control to user. In this mode, Network admin decides how many subnets needs to be created, in which region, what will be mask, dynamic routing mode (regional / Global) and MTU size. Here user can also ask for Flow logs and private Google access to be enabled.
It is possible to convert from auto mode to custom mod e, but not the other way around.
Subnets
When subnets are created, Admin must define one primary range and can also define up to 5 secondary ranges (optional).
Primary IP address range: Address assigned for this range is from RFC 1918 CIDR address spaces and should not overlap with same network. These IP are used to assigned VM primary internal IP address, VM alias IP address and the IP address of internal load balancers. In this range, only four Internal IP address are reserved for internal use.
Secondary IP address: Address can be assigned from RFC 1918 address space and can only be used for alias IP address. There is no address reserved in these Secondary IP address space.
Connectivity
We now know that VPC are global, and subnets are regional. We should know that VMs can have two types of IP address.
- Internal IP address: Assigned within the VM operating system. This IP address are always assigned to VM.
- External IP address: Assigned to VM but not valid in the operating system. This IP address can either be created automatically for you or you can create an IP address yourself. If you don’t ant to use this IP address, choose None when you request the VM.
Below figure explains the Communication flow:
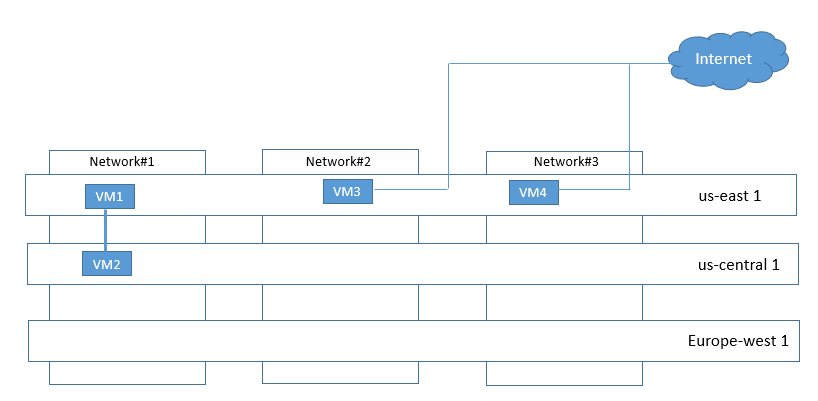
In above figure, VM1 and VM2 can communicate using internal IP. VM3 and VM4 need to communicate using external IPs.
Traffic between VM3 and VM4 does not need to traverse the internet but is routed through Google Edge router.
Calculating Cost
In GCP below are thumb rule for free cost traffic:
- Ingress Traffic
- Egress within same zones using Internal IPs.
- Egress to a different GCP service within the same region using an external IP address or an internal IP address.
Below are some traffic types for that customer will be charged.
- Egress between zones within the regions.
- Egress between regions
- Internet egress (VPN traffic is considered as Egress)





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.