EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USSD-Access Device Roles and Host Onboarding
Fabric Device Roles: As we have already discussed about the device roles in SD-Access Section, here we will give more details apart from it on some of the Devices roles only.
Fabric Borders: This is responsible for routing of traffic inside and outside of fabric. Any traffic who wants to go to outside fabric like DC, Internet, and any different fabric, it must go through the fabric Border router.
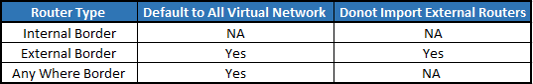
There are three types of fabric border, which can be configured now.
Internal Border Router: A border that router the traffic which is for that Enterprise network and want to go to DC or any other Fabric of same enterprise. These Internal Border router has these routes and it also registers them explicitly with control plane node.
External border Router: This type of External Border router routes the traffic to unknown address like Internet. This Router don’t register any routes to control plane.
Any Where Border Router: Border Router that work as both Internal Border as well as External Border Router. For External Destination, prefixes are registered to control plane node and for Unknown address, those are not registered to Control plane node.
Below configuration option shows for border Types.
Below figure shows the border configuration, with the check box enabled for external Border.
How to do Border Router Automation
There are two method to configure External Connectivity configuration o Border router.
Method 1: Manually and configure any VRF aware routing protocol such as BGP, OSPF etc.
Method2: Border Router automation via DNA Center.
Following parameters are required for Border Router automation workflow.
- Local AS Number
- IP Pool reversed in DNA and later will be subnetted in to /30 and will be used for SVI on border router.
- Transit/Peer Network: This network may be either an IP based transit network or SD-Access transit.
- External Interface that provide connectivity to transit network, and will be configured as trunk port by DNA Center.
- Virtual Network: VN or VRF need to be configured for Border Automation , and for each VN one SVI will be mapped or created and an eBGP Peering statement will be configured that points to Next Hop outside the border.
Below figure shows Border Automation configuration box in DNA Center.
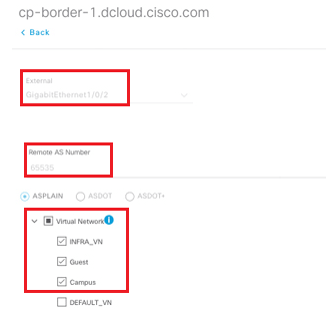
INFRA_VN is special VN that exits in SD-Access Global Routing table and does not correspond to a VRF on the fabric devices, providing connectivity access to wireless access points.
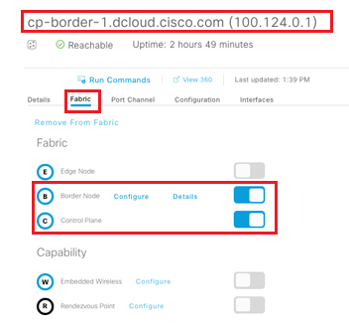
Border & Control Plane Collocation
In most of the SD-Access Design, Both Border Router and Control Node function can exits on same device and they can also be uses as a pair of redundancy and high Availability.
Below figure shows the border configuration box option for Collocated functions.
SVI Configuration of Edge Node by DNA Center
Once DNA Center is configured with the SVI , DNA Center Configured the Anycast gateway to all edge switches related to that SVI for wired and wireless both.
Below are some benefits of using Anycast gateway in SD-Access
- IP subnets spanning across the fabric, allowing for efficient use of IP address space
- Predictable and stable host mobility, for both wired and wireless, as hosts no longer need to change IP addresses or subnets when moving to a different fabric edge node
- Consistent configurations, as all SVIs on fabric edge nodes are configured the same way
- Efficient traffic flow, as the default gateway for every endpoint is always the connected switch
Below configuration will be pushed to Edge Switch by DNA Center. All Fabric SVI on all Edge node will have same MAC and IP , to support endpoint roaming and Mobility.
interface Vlan1143 description Configured from Cisco DNA-Center mac-address 0000.0c3e.e34a vrf forwarding Campus ip address 10.10.0.1 255.255.0.0 ip helper-address 100.100.0.1 ip helper-address 100.100.1.101 no ip redirects ip route-cache same-interface no lisp mobility liveness test lisp mobility 10_10_0_0-Campus-IPV4 end
Intermediate Node





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.