EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USData Redundancy Elimination
DRE is a compression technology that reduces the size of data transmitted over the WAN by eliminating redundant information from data streams. In Cisco SD-WAN, DRE uses a shared cache architecture where peers involved in compression and decompression share the same redundancy cache. DRE efficiently transmits the data stream across the Cisco SD-WAN overlay by replacing repeated data with shorter reference values or signatures. The local redundancy cache reconstructs the data stream at the receiving end for delivery to the destination client or server. Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN devices need to be deployed at both ends of the Cisco SD-WAN overlay tunnel to support this feature.
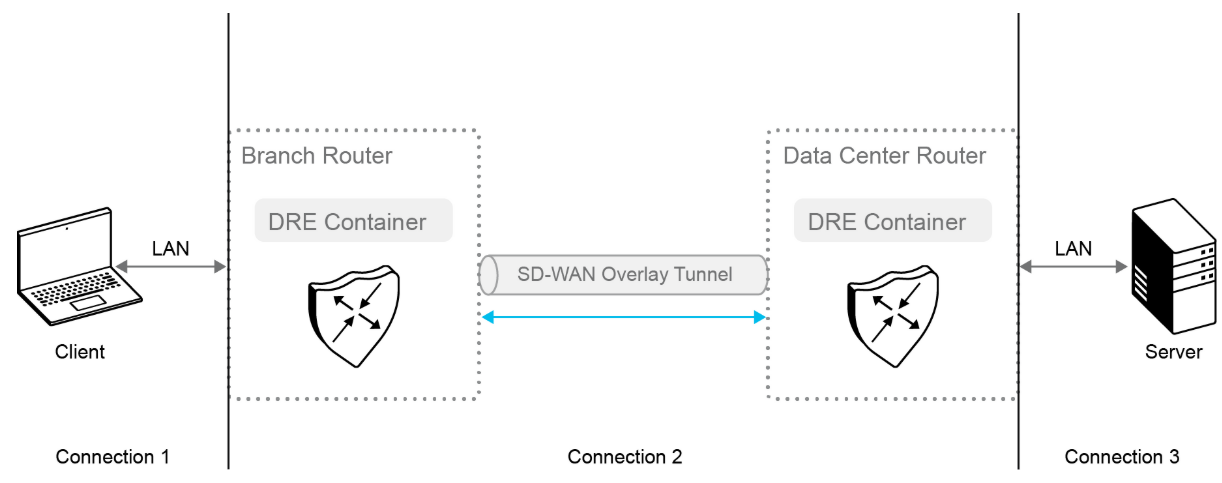
When DRE is configured, the TCP traffic is intercepted and separated into three connections, as shown in the following table:
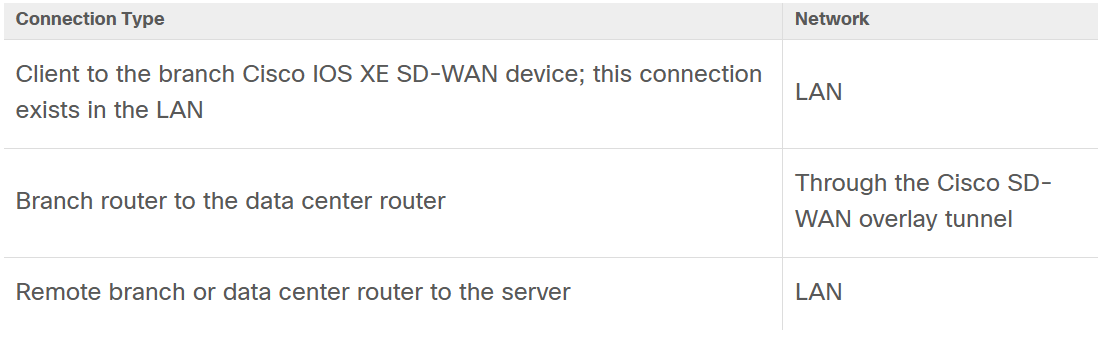
TCP connections in the LAN continue to send the original data. However, TCP connections through the Cisco SD-WAN overlay tunnel send data that is compressed by DRE. The DRE container in the Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN device at one side of the tunnel compresses the data before it is sent over the overlay tunnel. The DRE container in the Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN device at the other side of the tunnel decompresses the data before it is sent to the server at the remote branch or data center side.
DRE Components
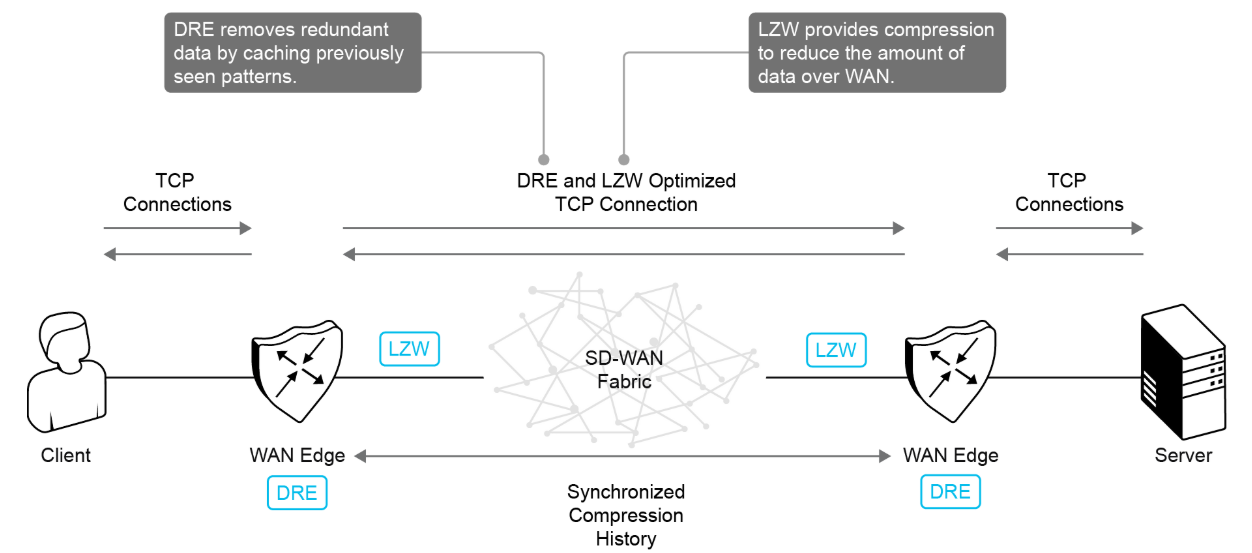
The DRE feature consists of two components:
-
DRE cache: The DRE cache uses secondary storage so that it can store a large amount of data. The DRE cache is stored on both sides of the WAN and is used by WAN Edge devices to decompress the data. The DRE cache in both devices (branch and data center) is synchronized, which means that if a chunk signature is present on one side, the other side has it as well.
-
DRE compression: DRE uses the Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) compression algorithm to compress data. DRE operates on large streams of data, typically tens to hundreds of bytes or more, and maintains a much larger compression history.
Another essential component of DRE is the DRE profile, which provides the flexibility to allocate resources to the DRE service based on the size of your branches and the number of connections required. DRE profiles are resource requirements and allocation combinations that enable resource assignment based on your connection requirements.
The following DRE profiles are supported:
-
Small (S)
-
Medium (M)
-
Large (L)
-
Extra large (XL)
Starting from Cisco IOS XE Release 17.6.1a, it is possible to configure Cisco Catalyst 8000V instances as external service nodes on supported Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) E-Series server modules. The Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (Cisco 4000 Series ISR) and Cisco Catalyst 8000 Series Edge Platforms house these server modules, which include integrated service nodes. By deploying Cisco Catalyst 8000V instances on these routers using supported Cisco UCS E-Series servers, it is possible to create hybrid clusters with both integrated and external service nodes. This feature enables routers with lower CPU and RAM to handle AppQoE services that require higher CPU, such as DRE.
You can install VMware vSphere ESXi 6.7 hypervisors on Cisco UCS E-Series server modules in Cisco 4000 Series ISR and Cisco Catalyst 8000 Series Edge Platforms. You can then install Cisco Catalyst 8000V on these servers to run AppQoE services.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.