EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USApplication - Aware Routing Overview
AAR tracks the network and path characteristics of the data plane tunnels between Cisco SD-WAN devices and uses the collected information to compute optimal paths for data traffic. These characteristics include packet loss, latency, and jitter.
The ability to consider factors in the path selection process other than factors used by standard routing protocols—such as route prefixes, metrics, link-state information, and route removal on the Cisco SD-WAN device—offers several advantages to an enterprise:
-
In normal network operation, the path taken by the application data traffic through the network can be optimized by directing it to the WAN links that support the required packet loss, latency, and jitter levels defined in the SLA of an application.
-
In the face of network outages or soft failures, performance degradation can be minimized. Tracking network and path conditions by AAR in real time can quickly reveal performance issues and automatically activates strategies that redirect data traffic to the best available path. As the network recovers from the soft failure conditions, AAR automatically readjusts the data traffic paths.
-
Network costs can be reduced because data traffic can be more efficiently load-balanced.
-
Application performance can be increased without the need for WAN upgrades.
The Cisco WAN Edge router supports up to eight transport locators (TLOCs), allowing a single router to be connected to eight different WAN transports. Each WAN Edge device in the SD-WAN environment advertises its local routes to the Cisco vSmart controller using the Overlay Management Protocol (OMP). The Cisco vSmart controller computes the best path selection algorithm for the entire SD-WAN environment and applies any configured centralized control policy before advertising the route selection to the WAN Edge devices.
The WAN Edge device installs the received OMP route in its forwarding table. For destination prefixes with multiple best paths, the WAN Edge router, by default, performs Layer 3 Equal-Cost Multipath (ECMP) load-balancing across four reachable next-hop TLOCs. The number of paths installed on the WAN Edge device can be increased to 16 if the next hop is reachable.
SLAs for each transport tunnel are calculated periodically using Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) probes by the WAN Edge router and are made available for advanced features like AAR to leverage and provide deterministic experience for business-critical applications.
The AAR allows the network administrator to evaluate the network path characteristics for the selected applications and set a preferred path if the SLAs are satisfied and a backup preferred path. The backup preferred path is chosen when no available WAN transport meets the specified SLA.
The AAR policy is configured in Cisco vManage GUI as a centralized data policy that maps one or more service-side applications to specific SLA requirements. The centralized policies provisioned in the Cisco vSmart controller are pushed to relevant WAN Edge routers for enforcement. The defined policy consists of match-action pairs, where the match statement defines the application list or the type of traffic to match, and the action statement defines the SLA action that the WAN Edge routers must enforce for the specified traffic.
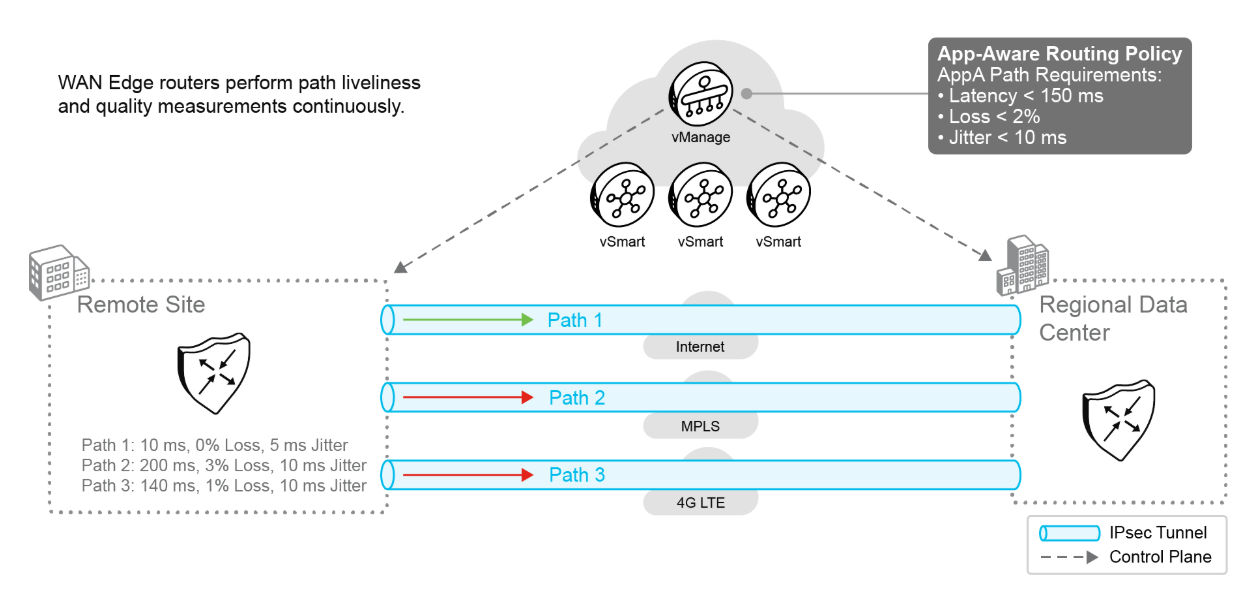
In the figure, Application A requires paths with less than 150 ms of latency, 2 percent loss, and 10 ms of jitter. The only path that adheres to these strict values is Path 1. Path 3 could become usable if the jitter drops below 10 ms.
Application-Aware Routing Components:
There are three components of Application Aware Routing discussed below:
Identification
Identify the Application to meet specific SLA, Create the Centralized policy based on 6 tuple, and configure it on vSmart controller which further passes its decision to vEdge router.
You define the application of interest and then create a centralized data policy that maps the application to specific SLA requirements. You match data traffic of interest by matching on the Layer 3 and Layer 4 headers in the packets, including source and destination prefixes and ports, protocol, and differentiated services code point (DSCP) fields.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.