EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USCisco SD-WAN Integrated Security Overview
This topic introduces Cisco SD-WAN integrated security overview, application-aware enterprise firewall, intrusion detection and prevention, intrusion prevention system (IPS) Snort engine architecture, and IPS Snort engine architecture.
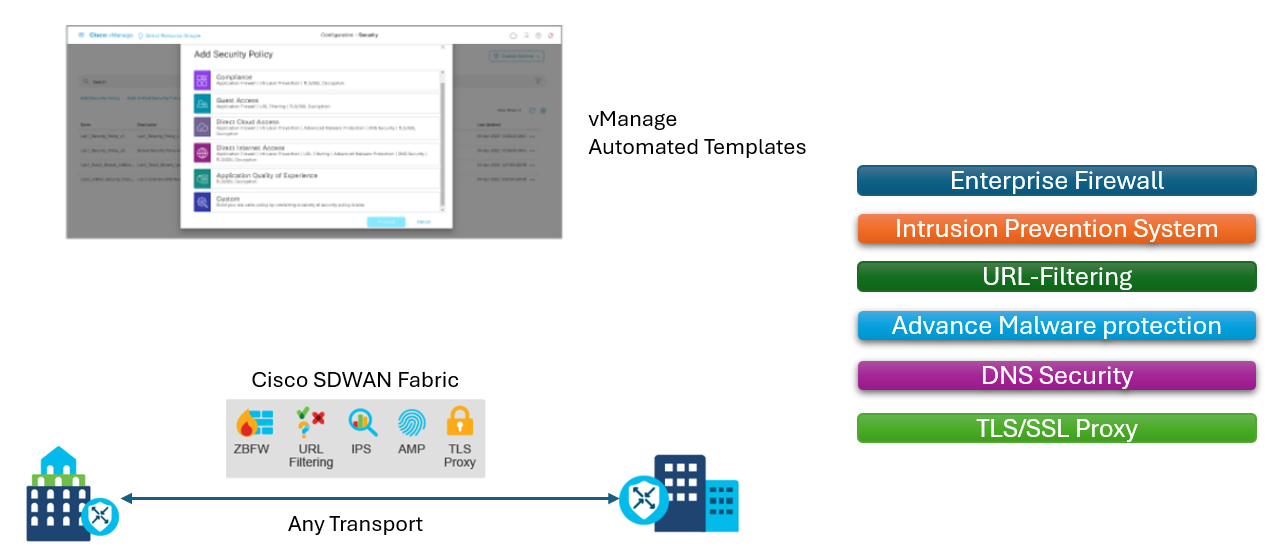
With business applications moving to the cloud and the increased use of direct internet access, branch locations require a wide range of security services. Protecting branch offices with the appropriate security capabilities is critical in today’s shifting IT landscape. Cisco SD-WAN brings the necessary security capabilities natively across the Cisco SD-WAN solution with the well-established single pane of glass management for both the Cisco SD-WAN and security services.
Cisco SD-WAN offers these integrated security services:
- Application-Aware Enterprise Firewall.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention based on the Snort processing engine and backed by Talos signature updates.
- Cisco URL Filtering with Bright cloud and Web root URL categorization and reputation.
- Domain Name System (DNS) and Web Layer security with Cisco Umbrella.
- Cisco Secure Endpoint (formerly Cisco Advanced Malware Protection [AMP]) with the Cisco AMP cloud and ThreatGrid.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) Decryption with TLS Proxy.
Application-Aware Enterprise Firewall
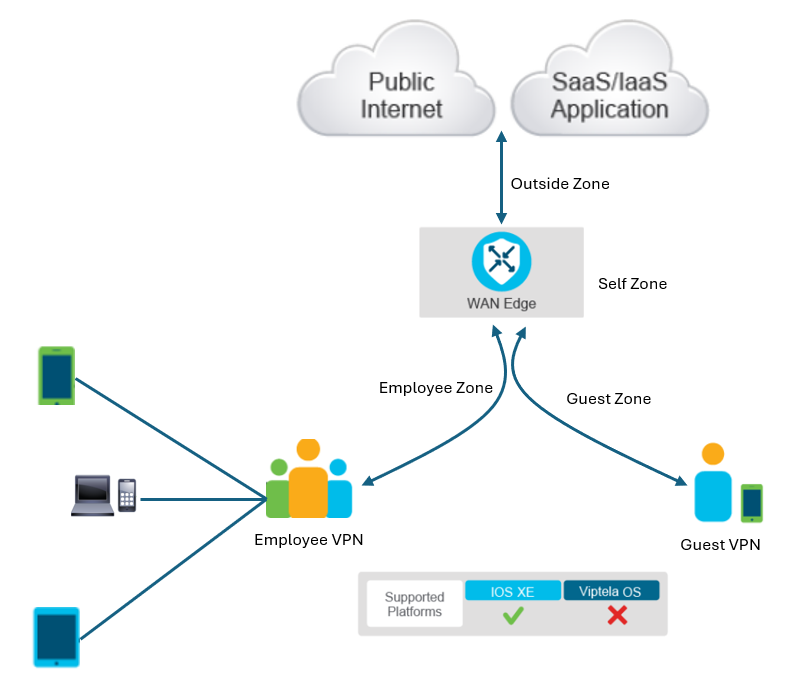
The application-aware enterprise firewall is a zone-based firewall supporting more than 1400 predefined applications along with the support for defining custom applications. Cisco IOS XE-based SD-WAN Edge routers support the application-aware firewall. Viptela operating system-based SD-WAN devices support the zone-based firewall without application awareness.
Within the Cisco SD-WAN solution, you map service-side interfaces to VPNs and VPNs to firewall zones. The firewall applies the rules to the zone pairs. A zone may contain multiple VPNs, but a VPN can belong to a single zone only.
You define the firewall policy as a set of rules matching specific conditions and applying an action. In addition to the defined rules, the policy applies the default action to any traffic not matching a specific rule.
The action applied to a rule can be Drop, Inspect, or Pass. The Drop action is self-explanatory. It simply drops the traffic. The Inspect action performs stateful packet inspection and allows return traffic for inspected connections. The Pass action forwards the packets without any inspection. This action is unidirectional, meaning it does not allow return traffic, and you must explicitly define the rule to allow return traffic for the Pass action.
The firewall can inspect traffic flows between users or devices within the same firewall zone and traffic flows between different firewall zones. You would commonly also use the firewall for direct internet access performing an inspection on internet-bound traffic to allow for the return connections.
In addition to regular zones that map to VPNs, the firewall supports Self-Zone policies to protect the routers themselves. Self-Zone policies protect management and control traffic sourced from or destined to the firewall itself. The firewall applies the Self-Zone policies across the device, not on specific interfaces.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention
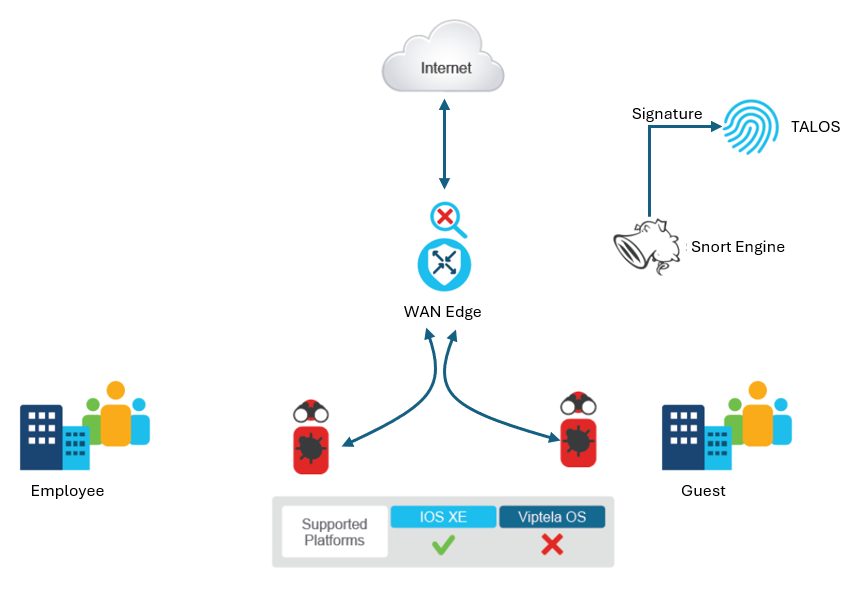
The intrusion detection and prevention in Cisco SD-WAN is based on a well-proven Snort engine and backed by Cisco Talos signatures. Cisco Talos signatures update automatically.
The Intrusion Detection and Prevention system work in either the detection or prevention mode, based on the configured policy.
The IPS engine performs these tasks:
- It monitors the network traffic and performs analysis based on a defined IPS signature set.
- It performs attack classification.
- It performs actions based on the matched policy rules.
When you enable Snort in the intrusion detection system (IDS) mode, it monitors the traffic and generates alerts. It does not take any action to prevent attacks. In IPS mode, in addition to the detection, the Snort engine enforces actions to prevent attacks.
The IDS or IPS system will analyze the traffic and report events to Cisco vManage or an external log server. You can use external third-party monitoring tools supporting Snort logs for log collection and analysis.
IPS Snort Engine Architecture
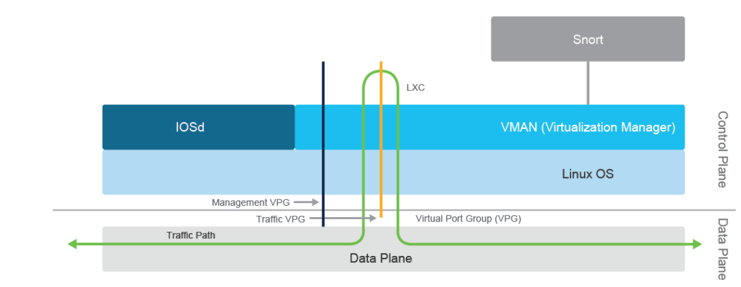
The IPS engine is deployed by using a security virtual image and only IOS XE SD-WAN devices support the feature. The Snort engine runs on a Linux Container (LXC) by using Control Plane resources. Using the Virtual Port Group (VPG) interfaces IPS engine redirects the traffic you want to inspect to the container.
There are two types of VPG interfaces:
- Management VPG: Used for logging and downloading signature updates from Cisco.com.
- Traffic VPG: Used for data traffic between the data plane and the Snort virtual container.
By using Cisco SD-WAN 17.5 or 20.5 and onwards, you can enable multiple instances of the Snort engine to provide reduced latency and improved performance.




LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.