EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USVLAN Encapsulation in ACI
There are two types of VLANs used in ACI
- External VLAN: Used for External Communication and Integration
- Internal VLAN: It is also called as Platform Independent Vlan whose scope is local to each leaf. ACI has no control how Platform VLAN is allocated to traffic going via leaf. APIC allocates PI VLAN per EPG, Per BD and these allocation is local to leaf and is different to each Leaf.
Cisco ACI fabric internally does not use VLANs as traditional switches but it translates externally connected VLANs to Flooding Domain, Bridge Domain and VXLANs. All of this is happening at the ingress to the fabric.
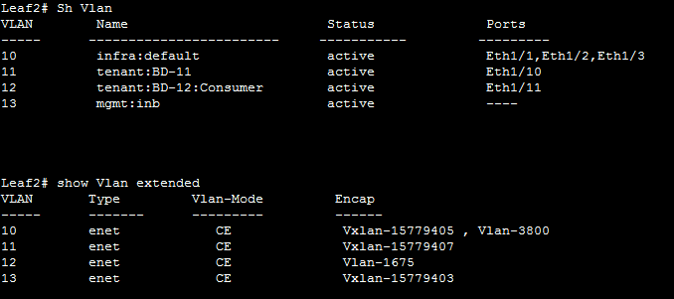
Here we can see the ACI has allocated the Platform VLAN to each VLAN which its receives from ingress port. Example from port Eth1/11, Traffic comes to Leaf with encapsulation of Ethernet vlan 1675 and upon receive, it allocates VLAN 12 randomly on that leaf switch.
show vlan extended output command you can see how internal VLANs are encapsulated to VXLANs or external VLANs. With this command, you can easily see which external VLANs are used on the particular leaf switch.
There are various Internal Platform VLAN used by ACI on each Leaf and they are independent to each other. Several VLANs exist on a leaf switch. There are two commands most commonly used for troubleshooting purposes: show vlan extended and show system internal eltmc info vlan brief. In the output of the later command you can see a table with several different VLANs:
Different Platform VLANs used in ACI are:
VlanId: is the PI (platform independent) VLAN of the system and is locally significant to each switch. This is the same VLAN as seen in the output of the command show vlan.
Hw_VlanId: is the VLAN used in ASICs but is usually not relevant for a user.
BD-VLAN: is used to represent a bridge domain and can link multiple FD-VLANs (encap VLANs) together with multiple hardware VLANs and internal VLANs. It is one forwarding aspect used by the Broadcom ASIC to determine if traffic should be locally switched or forwarded to the Northstar ASIC for processing. The BD-VLAN connects different local FD-VLANs to a single bridge domain, and is used on the Broadcom ASIC to determine the Layer 2 broadcast domain. If for example two different access_enc VLANs have the same BDVlan ID it means they belong to two EPGs that are part of the same BD.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.