EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USLISP Control & Data Plane Fundamentals
This topic will help you to understand LISP Traffic Forwarding and LISP packert flow in very deep dive detail.
LISP Control Plane:
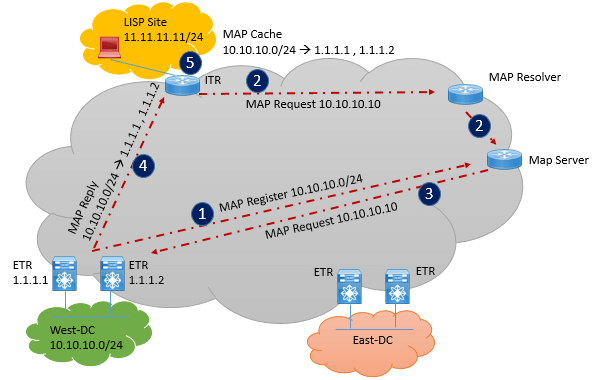
Following are the steps which describes how EID to RLOC mapping is shared between mapping database.
- In Every 60 Seconds, West ETR will register EID subnet 10.10.10.0/24 to mapping server by Map-registration message.
- Now let’s assume that LISP site does have any mapping available for West-DC EID, now from LISP Site, when a client wants to communicates to West-DC, a map-request is sent by remote LISP ITR to map-resolver which will send that request to Map-Server.
- MAP-Server forwards the original Map-Request to West-DC ETR, in this ETR which is locator 1.1.1.2.
- ETR will sends to ITR a map-reply to ITR which contain reply for requested information.
- Now once Map-Reply is received by ITR for LISP site, ITR installs the mapping information in its local map-cache and starts encapsulation traffic towards Data Center EID destination.
LISP Data Plane:
Let’s suppose Client at LISP remote site want to access dclessons.com, and gets ip 10.10.10.10 after DNS resolution.
Now traffic to 10.10.10.10 from host reaches to ITR, and ITR will look up at routing table for destination 10.10.10.10, since destination is EID subnet, and hence its lookup fails as it is not present in RLOC space, which triggers LISP control plane.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.