EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USLISP Architecture Overview
LISP Roles
To understand LISP in details, we need to understand the LISP roles in bit details.
Tunnel Router:
Tunnel router are those routers which are placed at edge on LISP network. The tunnel router are responsible for encapsulating and decapsulation of EID traffic in to RLOC address tunnels. These tunnel router also Query to mapping data base system and populates its own mapping database table. Based on direction of traffic ingress and egress, the tunnel router are further classified in to following routers
- Ingress Tunnel router
- Egress Tunnel router
Ingress Tunnel Router:
Ingress tunnel router are those router which acts as entry point of traffic from any LISP site to overlay. It is the ITR who query to mapping database system to get the EID and its location mapping information and then encapsulate the traffic to destination RLOC in order to send it to overlay network and further cache the information to local mapping table. But before sending traffic, ITR must check whether the RLOC is reachable over underlay.
Egress Tunnel Header:
An ETR is a traffic exit point from LISP overlay network and it decaptsulate the traffic they receive. ETR are responsible for registering the EID to RLOC mapping, their priorities, and weights to mapping database system with help of map-register message.
ETR are responsible for replying to Queries about EID mapping they have registered only if ETR is part of mapping database system and authoritative for replying map resolution Queries.
Proxy Tunnel Router: They are those router which connect non-EID prefixes or Non-EID prefix site to EID prefixes or EID prefixes sites.
There are two types of PTR routers:
Proxy Ingress Tunnel Router: Those router which receives traffic from non-EID area to EID Prefixes site. Their function are similar to ITR as they also resolve the mapping for destination EID and encapsulate the traffic to send it to destination. But the basic difference between ITR and PITR is that, ingress PITR encapsulate traffic towards EID regardless source of traffic is an EID or not, an ingress PITR does not check source because its role is to receive the traffic from RLOC sources and forward it to EID destination.
Proxy Egress Tunnel Router:
A PETR decaptsulate the traffic tunnel to RLOC and its main purpose is to provide connectivity for EID sources to reach destination in RLOC space outside LISP network. A PTER does not register any address with mapping Database system.
Mapping database System:
Mapping database is a database bank which contains EID to RLOC mapping. There are two roles defines in mapping database system
- Map-Server (MS)
- Map-Resolver (MR)
Map-Server: It receives all EID registration that it get and it installs it to the EID to RLOC mapping in its mapping database.
Working of Mapping –Server is well defined in below figure
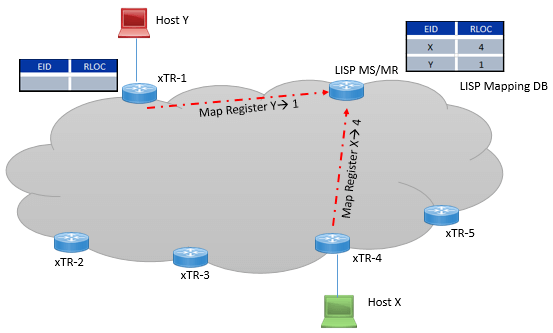
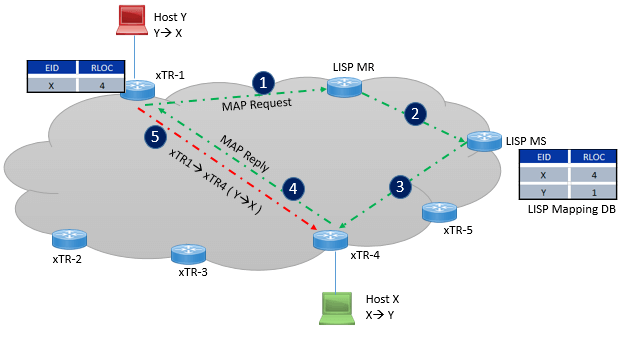
Map-Resolver: Map-Resolver is the interface between mapping database system and ITR. As soon as Map-resolver receives a map-request, it send the map-request to the Map-server and then MS sends to authoritative ETR. Now once authoritative ETR receives request, it respond directly to Map-Requester. And ETR will update its mapping Cache with information it received.
LISP DATA PLANE





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.