EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USTraffic Flow Unicast Forwarding (Bridging)
Traffic Flow Unicast Forwarding (Bridging)
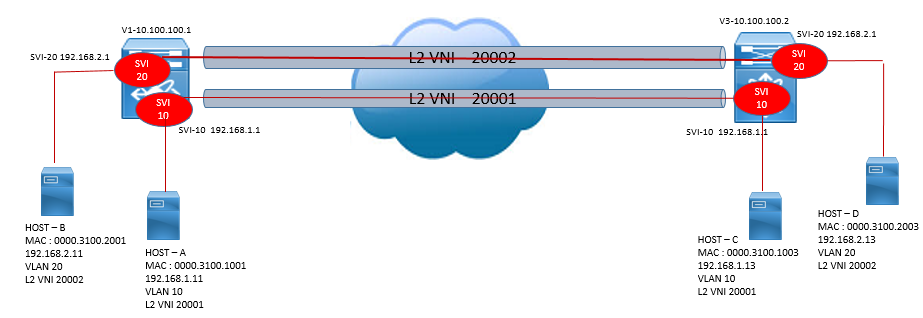
This Section explains how unicast traffic forwarding is done in when source and destination are in same subnet. VTEPs V1 and V3 are associated with NVE interfaces with IP addresses 10.100.100.1 and 10.100.100.2 respectively.
Below topology is used for explanation.
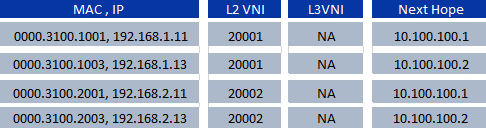
When we are running BGP-EVPN , then as soon as local end points are learned on local switch , the respective MAC address is proactively distributed during BGP updates to all neighboring VTEPs. Following is the information that BGP-EVPN protocol would have.
We can verify this able table information by following ways:
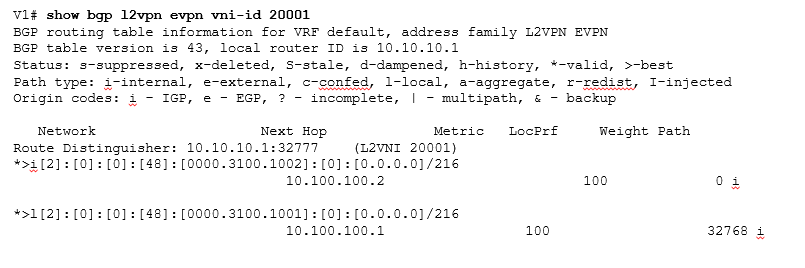
To verify that the MAC address or MAC/IP prefix (Route type 2) has been received, This information is installed in an EVPN instance, which is also called a MAC VRF.
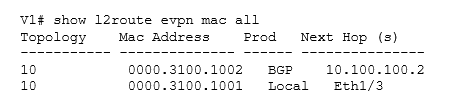
Once the Layer 2 “routing” table has been verified with the appropriate MAC prefixes, our next step is to ensure that similar entries should be present in the MAC address table at the VTEP itself, as shown in below figure
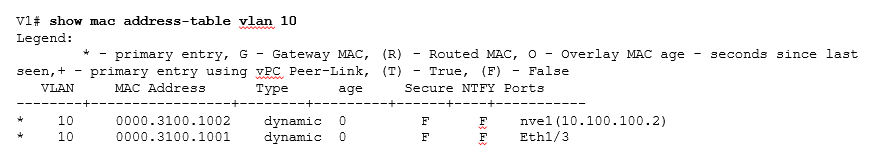
Now Control plane is populated, let take an example that Host A (192.168.1.11) connected to VTEP 1 want to communicate with host C 192.168.1.13 connected to VTEP 2 and both host are in same VNI 20001.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.